Case Report - Ophthalmology Case Reports (2023) Volume 7, Issue 5
Rhabdomayosarcoma: A rare disease found in children
Shripat Narayan Dixit*, P Mansoori, R Kanash, Gomabai Netralaya Nimach
Department of Ophthalmology, Gomabai Eye Hospital, Madhya Pradesh, India
- Corresponding Author:
- Shripat Narayan Dixit Department of Ophthalmology, Gomabai Eye Hospital, Madhya Pradesh, India, E-mail: shripatdixit@gmail.com
Received: 19-Aug-2020, Manuscript No. OER-20-17711; Editor assigned: 24-Aug-2020, PreQC No. OER-20-17711 (PQ); Reviewed: 07-Sep-2020, QC No. OER-20-17711; Revised: 30-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. OER-22-67667(R); Published: 28-Dec-2022, DOI: 10.35841/oer-6.8.140
Citation: Dixit SN, Mansoori P, Kanash R, et al. Rhabdomayosarcoma: A rare disease found in children. Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022;6(8):140
Abstract
In this disease malignant (cancer) cells form in muscle tissue. Certain genetic conditions increase the risk of childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma. It is mainly four types: Embryonal, alveolar, spindle cell and pleomorphic. A rare disease found in children rhabdomayosarcoma, is an embryonal tumor and it mostly common in children around or below the age of seventeen years or so. We saw a patient in last week of June 2020 and it was lockdown period due to COVID-19. Initially the child was diagnosed Rhabdomayosarcoma in our hospital but further investigations were carried out to make it confirm. We want to present this case as a case study to see the characteristics about the disease.
Abstract
In this disease malignant (cancer) cells form in muscle tissue. Certain genetic conditions increase the risk of childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma. It is mainly four types: Embryonal, alveolar, spindle cell and pleomorphic. A rare disease found in children rhabdomayosarcoma, is an embryonal tumor and it mostly common in children around or below the age of seventeen years or so. We saw a patient in last week of June 2020 and it was lockdown period due to COVID-19. Initially the child was diagnosed Rhabdomayosarcoma in our hospital but further investigations were carried out to make it confirm. We want to present this case as a case study to see the characteristics about the disease.
Keywords
Rhabdomayosarcoma, Muscle tissue, Cartilage, Sarcoma.
Introduction
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a type of sarcoma. Sarcoma is cancer of soft tissue (such as muscle), connective tissue (such as tendon or cartilage), or bone. Rhabdomyosarcoma usually begins in muscles that are attached to bones and that help the body move, but it may begin in many places in the body.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common type of soft tissue sarcoma in children. A sign of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma is a lump or swelling that keeps getting bigger [1].
In children below seven it is mostly Embryonal and it has no symptoms in initial stage. Slowly it begins to increase in size then certain sign and symptoms are manifested. Signs and symptoms may be caused by childhood rhabdomyosarcoma or by other conditions. There may be small swelling or lump which keeps on increasing in size. This is painful and bleeding from nose and in urine also may be here [2].
Case Presentation
It is mainly four types’ embryonal, alveolar, spindle cell and pleomorphic. Risk factors for rhabdomyosarcoma include having the following inherited diseases:
• Li-fraumeni syndrome
• Dicersyndrome
• Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
• Costello syndrome
• Beckwith-wiedemann syndrome
• Noonan syndrome
Children who had a high birth weight or were larger than expected at birth may have an increased risk of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcom. Signs and symptoms may be caused by childhood rhabdomyosarcoma or by other conditions [3]. The signs and symptoms that occur depend on where the cancer forms. Check with your child's doctor if your child has any of the following, although in early period of the tumor may not show the signs but in advance stage one can see the following sign and symptoms:
• A lump or swelling that keeps getting bigger. It may be painful.
• Proptosis or prominent eyes.
• Headache and vomiting or nausea.
• Trouble urinating or having bowel movements.
• Blood in the urine.
• Bleeding in the nose, throat, vagina, or rectum.
Essential investigations for diagnosis of childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma
X-ray, CT scan, MRI and histopatholical tests of the tissue were carried out but some more tests can be done as per clinician advice or as per need.
Stages: Clinician has to decide the risk factor form low, intermediate and high risk depending upon the stage of the tumor and patient’s medical history [4].
• After childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma has been diagnosed, treatment is based in part on the stage of the cancer and sometimes it is based on whether all the cancer was removed by surgery.
• There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
• Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body.
• Staging of childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma is done in three parts.
• There are four stages based on the size and location of the tumor in body.
Results and Discussion
Once childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma has been diagnosed, treatment to be given as per the Cancer treatment: The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the tissue or to other parts of the body is called staging. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The clinician will use results of the diagnostic tests to help find out the stage of the disease.
Treatment for childhood rhabdomayosarcom is based in part on the stage and sometimes on the amount of cancer that remains after surgery to remove the tumor. The pathologist will use a microscope to check the tissues removed during surgery, including tissue samples from the edges of the areas where the cancer was removed and the lymph nodes. This is done to see if all the cancer cells were taken out during the surgery [5-7].
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood
• Tissue: The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
• Lymph system: The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
• Blood: The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
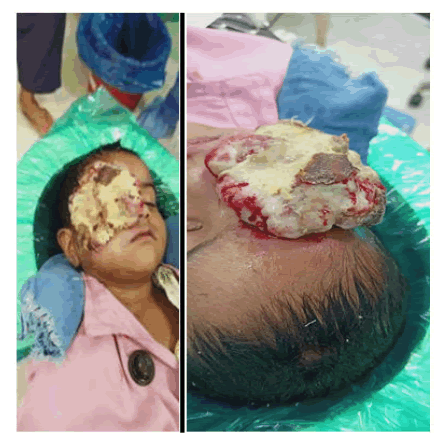
This child has been consulted at his local place in a medical college in central India, but doctors were not very much comfortable to operate because of the size of tumor and then she was referred to consult at a higher centre where this can be managed or excised. Therefore she reported at our centre where she underwent exentration (Figure 1).
To create the awareness in the medical fraternity about the deadly disease. A three old baby girl first reported at our hospital on 23rd June 2020 with complain of extra growth in the right eye with severe pain. On examination she was diagnosed suspected rahbdomayosarcoma which was later confirmed with differential diagnosis and CT scan orbit and brain etc. Left eye was within normal limits. In one week that lumps became very big and covered her half face on right side.
Child was then advised to undergo for Exentration as early as possible under full sedation or general anaesthesia to avoid any further spreading of the disease. Child was anaemic also therefore blood transfusion was done before her surgery.
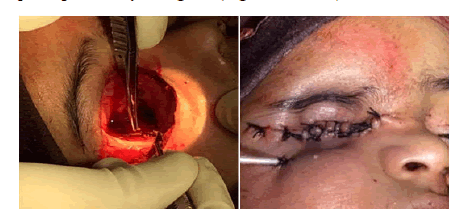
Intra operative: Tumor was removed surgically with complete exentration and cleaned all the fiber to avoid any secondary growth of the tumor. Exentration surgery went uneventful and post op recovery was good (Figures 2 and 3).
Conclusion
In such type of disease it is very important to start the treatment timely to avoid any serious life threat. In subsequent post op follow ups showed normal recovery and patient was sent to oncologist for further management.
References
- Hayes Jordan A, Andrassy R. Rhabdomyosarcoma in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2009;21(3):373-78.
- Sokolowski E, Turina CB, Kikuchi K, et al. Proof-of-concept rare cancers in drug development: The case for rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene. 2014;33(15):1877-89.
- Grufferman S, Wang HH, DeLong ER, et al. Environmental factors in the etiology of rhabdomyosarcoma in childhood. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982;68(1):107-13.
- Shields JA, Shields CL. Rhabdomyosarcoma: Review for the ophthalmologist. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003;48(1):39-57.
- Kumar V, Chaudhary S, Kumar M, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma of biliary tract: A diagnostic dilemma. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2012;3(4):314-16.
- Hicks J, Flaitz C. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and neck in children. Oral Oncol. 2002;38(5):450-59.
- Zampieri N, Camoglio F, Corroppolo M, et al. Botryoid rhabdomyosarcoma of the biliary tract in children: A unique case report. Eur J Cancer Care. 2006;15(5):463-66.