Case Report - Gynecology and Reproductive Endocrinology (2021) Volume 5, Issue 2
Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorder (PAS): Challenge that demands team work and anticipation, a clinical case report
Javier Enrique Oviedo Venerio1*, Giblin Gary2, Torrez Magdaly2
1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Danilo Rosales Hospital, León, Nicaragua
2 Department of Family Medicine, National Autonomous University of Nicaragua, Managua, Nicaragua
- Corresponding Author:
- Dr. Javier Enrique Oviedo Venerio
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology ,
Danilo Rosales Hospital,
León,
Nicaragua
E-mail: mkjoharii@gmail.com
Accepted date: 23rd July, 2021
Citation: Venerio JEO, Gary G, Magdaly T. Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorder (PAS): Challenge that demands team work and anticipation, a clinical case report. Gynecol Reproduct Endocrinol 2021;5(2):5-6.
Abstract
Diagnosis and treatment of placental accreta is a real challenge especially in countries with limited resources. The successful outcome depends on prenatal diagnosis and preparation for childbirth. We describe our experience with 5 cases in the HEODRA School Hospital, Leon Nicaragua. All case with the same risk factors as placenta Previa and history of previous caesarean section. In one patient with two curettage story. These two variables carry high suspicion. The origin of the global problem is the high caesarean section rate. According to hospitals, the rate of cesarean sections in Nicaragua ranges between 30 and 45 percent, being considered as the origin of the problem of placental accreta. The risk of placental accreta with placenta Previa increases in relation to the number of caesarean sections. It reaches up to 40 percent in patients with two previous C. section. Although Institutional Norm is to perform the caesarean section at 35 weeks in case of placental accrete, in all our cases delivery was performed at 37 weeks, we consider late prenatal diagnosis.
Keywords
Placental accreta, Caesarean section, Previous placenta, Nicaragua heodra.
Introduction
Ultrasound represents the technique of choice for the diagnosis of placental accreta in the second and third trimester where the presence of placental lagoons is the sign that has the highest sensitivity of 93 percent [1-4]. It is associated morbidity is mainly caused by the high risk of massive hemorrhage, infection, and injury to adjacent organs. Estimated blood loss is three to five liters. Representing a high Maternal Mortality of 7 percent in developed countries [5].
Placental Acreta is classified according to the degree of invasion to the Myometrium of corial villi. Acreta the chorial villi inserted directly over the Myometrium. It’s reprented 80 percent of cases followed by placenta increta where they invade Myometrium and represent 15 percent of cases. Placenta percreta account for five percent and invade bladder serous and other organs [5,6].
The purpose of this case report is to describe our experience in five case placentae accrete during a period of 3 years. By sharing our clinical experiences, we learn. The author considers it is important to share and describe how to diagnose and treat this true obstetric emergency.
They are referred patient of the high-risk service to perform Doppler ultrasound due to presenting a previous placenta and history of previous C-section, with suspected acretism to be ruled out. The author related and checked ultrasonography findings with surgical findings and pathology reports. Surgical time, blood loss and need for transfusion. General data of the file at the same time ultrasound and after the surgical procedure. This information was recopilated with resident collaboration and the permission of the patient and institution.They are referred patient of the high-risk service to perform Doppler ultrasound due to presenting a previous placenta and history of previous C-section, with suspected acretism to be ruled out. The author related and checked ultrasonography findings with surgical findings and pathology reports. Surgical time, blood loss and need for transfusion. General data of the file at the same time ultrasound and after the surgical procedure. This information was recopilated with resident collaboration and the permission of the patient and institution.
Clinical Case
The average age was 28 years old. With 37 weeks of pregnancy. All case with the same risk factors as placenta Previa and history of previous caesarean section. In one patient with two curettage story. The diagnosis of primary care by ultrasound was Occlusive placenta Previa without current history of transvaginal bleeding. In all case hysterectomy was performed after caesarean section with multidisciplinary team.
Results and Discussion
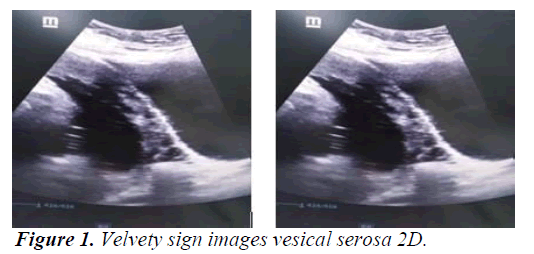
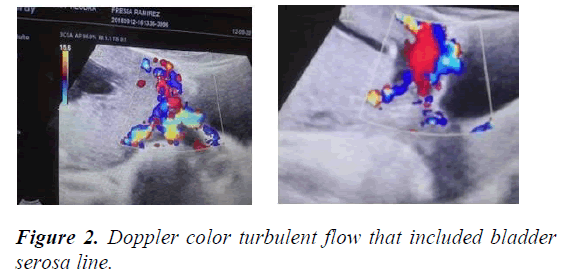
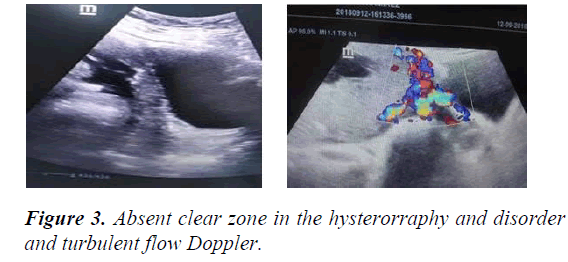
Main ultrasound finding in order of frequency are lacunar beds in all cases. Followed by Doppler color turbulent flow that included bladder serosa line and absent clear zone in the hysterorraphy site (Figures 1-3). In all cases it was observed by ultrasound fine lines like velvety hair were noticed between the placenta and serous bladder distorting the line of the bladder serosa. Surgical macroscopic finding is bladder serosa distorted with marked vascularization and tortuous vascular network. In all case is active red code. Multidisciplinary team participation. Blood loss during cesarean delivery was 2000 ml. All case they needed blood transfusion average four globular packages.
Shock index greater than 1. Average Hemorrhagic shock classification type 3, and all patient required Intensive Care after hysterectomy. Average surgical time 140 minutes [3]. We made in all case caesarean section with wide longitudinal incision. Body histerotomy incision with product extraction leaving the placenta and early uterine vessel clamping. A case of Percrete Placenta confirmed by pathology biopsy.
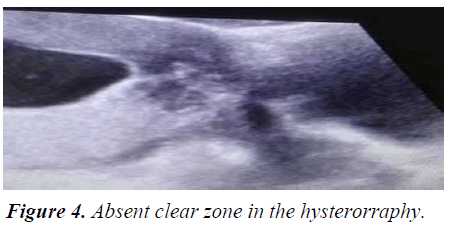
No bladder injury reported but one patient presented bowel laceration that require repair in the same surgical time. There were no maternal deaths. In all case the fetal Doppler ultrasound was performed late near 37 weeks’ gestation. This complicates the doctor on duty with great coordination effort. We learned is necessary share case and ultrasound image and surgical finding to improve early diagnosis. One of the strengths identified is the communication through What UP Groups, where all of the medical and administrative team are in action according to roll (Figure 4).
Conclusion
The Success of placental accreta treatment requires identifying risk factor, such as placenta Previa and history of previous caesarean section, or history of curettage. In this context it is mandatory to perform an early fetal Doppler ultrasound. This also depends on the Anticipation and with the most experienced and Multidisciplinary team to avoid Emergency situation. Lacunar beds with turbulent Doppler color flow and clear zone absent is the most frequent presentation ultrasound image.
We consider in some case is a good choice delay the surgical treatment in patient without bleeding or labor until all the human team and materials is completed. Blood bank should always maintain emergency backup.
In our patient IL-6 levels increased before tocilizumab. After tocilizumab therapy, there was not any significant decrease ın IL-6 levels, neither any symptoms like fever or decrease. Despite the second dose of tocilizumab, his clinical status did not change, and the patient’s respiratory tract culture. Tocilizumab therapy in the early days of the disease might be responsible for this clinical situation.
The cornerstone in prevention is promote institutional efforts to reduce the rate of unnecessary cesarean sections. also efforts at early ultrasound diagnosis, taking into account the variables always present, history of cesarean section with placenta Previa or history of curettage because is the origin of the problem.
Patients with HIV are more susceptible to respiratory infections while HIV is not well treated. At the same time, immune deficiency status in HIV patients may lead to less detectability of SARS-CoV-2 virus and worse clinical condition.
Early detection of symptoms for mucor like cheek swelling, blackening etc got to be reported immediately. Furthermore, if a CT scan finds a mucormycosis fungus, then there's a gold standard treatment and also removing dead tissue through surgery. Clinical suspicion and prompt treatment are fundamental to realize the cure of the disease. More studies are necessary to determine if these two pathologies are related.
References
- Analysis of the Country Situation as of 2014. United Nations Guatemala. 2014.
- Protocols for the Care of Obstetric Complications. SITEAL. 2018.
- Tagle M, Nolte C, Luna E et al. Coexistence of celiac disease and autoimmune hepatitis: Case report and literature review. Rev Gastroenterol Perú. 2006;26:80-3.
- Pairazaman PE. Placental Anomalies. Hospital Clinic of Barcelona. 2012.
- Costa JA, Rito M, Lopes L. Traumatic carotid-cavernous fistula with contralateral proptosis: Clinical case. Neurosurgery. 1993;4: 313-15.
- Guidelines for the care of the main obstetric emergencies. Pan American Health Organization. 2018.