Research Article - Journal of Finance and Marketing (2018) Volume 2, Issue 3
Assessment Of The Effectiveness Of Accounting Information As A Tool For Management Decision In Manufacturing Companies In Osun State, Nigeria
Akinniyi A Bukunmi*, Akinola A Olusola, Olagunju AdebayoDepartment of Accounting Banking and Finance, Osun State University, Okuku Campus, Osun State, Nigeria
- Corresponding Author:
- Akinniyi A Bukunmi
Department of Accounting Banking and Finance Osun State University
Okuku Campus, Osun State Nigeria
Tel: +2349036674524
E-mail: azeez.bukunmi@yahoo.com
Accepted date: June 15, 2018
Citation: Bukunmi AA, Olusola AA, Adebayo O. Assessment of the effectiveness of accounting information as a tool for management decision in manufacturing companies in Osun state, Nigeria. J Fin Mark. 2018;2(3):1-9.
DOI: 10.35841/finance-marketing.2.3.1-9
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Finance and MarketingAbstract
This study examined the relationship between accounting information and management decision with emphasis on the effect of accounting information on economic order quantity decision, human resources management decision and marketing decision of selected manufacturing organizations. Data were sourced primarily with the aid of structured questionnaire from one hundred and fifty top management staff statistically selected from the selected manufacturing companies in Osun State, Nigeria. Empirical research designs and inferential analysis were carried out with the aid of statistical package for social sciences (SPSS version 20). The t-test results carried out confirmed a positive relationship between accounting information and management decisions in manufacturing organizations. Based on this, the study recommends that adequate awareness and effective utilization of various accounting tools should be incorporated into decision making processes as this will impact on human resources investment and enhance appropriate strategies for introduction of new products into markets.
Keywords
Accounting information, Economic order quantity, Marketing, Management decision, Manufacturing companies, Product development
Background of the Study
Accounting information is the type of information generated by an organization to be used as a basis or tool for decision making. Availability of information at the right time is paramount to the success of every business organization and failure to leverage on accounting information often proof counterproductive towards the achievement of goals in organizations Accounting information are qualitative and quantitative details in readable and understandable form to assist various stakeholders. This can as well be related to the record generated from organization’s transactions at the finance and account section to be used as a tool or resources upon which decisions of the organization are taken towards accomplishment of set goals and objectives. This information cut across areas like financial information, non-financial information, managerial information etc.
According to Royaee et al. [1] accounting can be defined as the process of keeping adequate record of financial and non-financial transactions made, properly classifying them, ensuring its detailed evaluation and insightful analysis, and carefully ensuring that its report to users are timely for possible decision making. It helps to process documents of business financial performance e.g. payroll, expenditure, other obligations etc. On the other hand, information is a processed data. Similarly in Law [2], information was defined as that which is assigned to data by means of convention used in their representation. It consists of raw data that has been retrieved and processed which can be used for informative and inference purpose or as a basis of forecasting and decision making.
The survival of a business enterprise (both individual and corporate) depends solely on the quality of decisions (right) it implements. This decision is influenced by output from the accounting system in place, supplied to the management. An appropriate, accurate, detailed and up to date presentation of accounting information is indeed a product of an organization whose affairs is administered with good decision. Accounting information can also be classified into financial (quantitative) and non-financial (qualitative) information which is used by decision makers. Managers make use of financial and nonfinancial information in making decisions e.g. strategic, tactical and operational, and the application of these information demands a careful execution towards the accomplishment of the organization’s goal and objective. More so, this information when properly analyzed and employed could influence financial performance of an entity, and lack of such financial and accounting information to guide the management both in short term and strategic decisions could be vital to the survival of an entity. In any entity whether merchandise or manufacturing outfit, there are varying constituents interests contribution to the smooth operations and success of such an entity and this in the opinion of Freeman [3] is known as stakeholders. The stakeholders are those that influence the firm and those that are influenced by a firm.
These stakeholders can further be classified into external and internal users. Creditors, potential investors, bond/stock holders, government taxing agencies, suppliers and customers are all under external users while internal users of accounting information are individual employees, department, regions and top management of an organization. The type of information each of these user needs will depend on the kind of decisions they want to make. e.g., managers needs detailed information about their daily operating cost in order to control the operations of the business and in the determination of selling price, employees as well needs this information to determine the ability of the company to pay their salaries and determine the going concern status of the company, investors needs it to know whether the company is worthwhile, while creditors needs the information to determine the credit worthiness of the company.
However, for accounting information to be useful for management decision, it must meet the basic requirements of Relevance, Reliability, Comparability, Consistency, etc., and this information may be in form of accounting ratios which are used in estimating and obtaining insight knowledge of present state of affairs of an organization as well as predictive information of business and financial direction of an organization. These ratios provide wide acceptance across industries as performance indicator. Ratios such as: Profitability, Liquidity or Short term solvency, Debt or Leverage, Activity or Efficiency, Investment/Potential and Actual Growth, Gearing or Long term financial stability ratios are widely used to provide management with inside knowledge of an organization’s strength and weakness [4].
Improper awareness and bad attention to accounting information and its application has given birth too many problems like: poor planning which result to poor decision making (especially in the allocation of resources). The realization that decision can make or mar the survival of any organization and positive influence of accounting information on rational decision is the central theme of this study. It is on these premises that this study wishes to access the effectiveness of accounting information as a tool for management decision using data from the selected Nigeria listed manufacturing sector. The dependent variables to be considered for this study are: the economic order quantity, human resources management and marketing decision while accounting information represent the independent variable.
Theoretical Review
Signaling theory
The signaling model was first proposed by Brennan and Copeland [5]. In this theory, financial information cannot be overemphasized to be one of the means through which the passage of information is successfully made to users (especially from managers to stockholders). A hypothesis was built by Fama et al. [6] which suggest that the announcement of splits by a company could foster the reduction of any asymmetric information in existence between stockholders and management. Olaleye et al. [7] explained in their article that the signaling hypothesis suggests that an announcement of a stock dividend conveys new information to the market. An examination of Foster and Vickrey’s paper on daily returns around announcement dates in 1978 was made by Pathirawasam. The motive primarily lies in the determination of whether the announcement of stock dividend influences investor’s expectation in the area of future firm’s prospects. The analysis covers for 82 stock dividend announcements, the daily market model residuals during those announcement days. News announcements and cash dividend announcement for 3 days of declaration were used to control the sample. Arthurs et al. [8] discover from their findings that signaling and initial public offerings (IPOs) supported the signaling theory and can be used to further explain the signaling theory with regard to bonus issues and stock splits. During the announcement of bonus shares and stock splits, the necessary signals before the announcement, breeds in shareholders’ and other user’s sensitisation. Therefore, the existence of these splits in a company denotes its effectiveness and efficiency in operation and as a result, tells greatly on its huge markup potential. It is also issued by managers in order to ensure confidence is restored and retained to a large extent by the company. This act therefore, necessitates an increase in the number of its shareholders.
Appropriate disclosure of accounting information serves as a great signal to its users as it could be used in making a more effective decision for the company. This study found this theory most relevant as it provides theoretical support for the objective of the study.
Clark theory of profitability
The analysis of a profit-less economy and its key features constitutes the early postulation of Clark’s theory. The comparison of a profit less economy with a profit-generating economy resulted in the identification of significant differences that indicate the causes of profit. Adesina et al. [9] have asserted that ‘static state’ denotes a profit- less economy where market is assumed to be perfect and all factors are constant with resistance to change. Here, the absence of monopoly and entrepreneurial efforts, perfect mobility and all impediments to perfect competition are dissolved. A relevant change in the number of populace and per capital income will equally bring about a corresponding dwindling in income and interest rates and the resulting effect on the economy will necessitate a settling back to a static state.
According to Clark theory, competition has the tendency to eliminate profit or loss and bring the value of economic goods to equality with their cost. Real economies as noted by Clark will, however, not buffer such changes instantaneously as there will necessarily be a time lag. Adesina et al. [9] have claimed that profit is hence a transitional phenomenon, untransformed increments of wages and interest. Its temporary nature demands from the entrepreneur a dynamic endeavor to seek out or generate opportunities on which he can capitalize. This process is summed up in Clark's statement that dynamic forces, then, account today for the existence of an income that static forces will begin to dispose of tomorrow. Since change is the representative of cause of profit according to Clark’s analysis, entrepreneurs are encouraged to closely be on the lookout for any threatening changes as it emanates in the economy. Also, timely information to enable them monitor the change as it occurs in the economy is essential.
Contingency theory
Contingency theory suggests that the incorporation of a less-rigid design of accounting information system (AIS) should be promoted by an organization in order to be strategically prepared for any influence which may arise from environment, and organizational structure that poses threat to an organization. Accounting information systems also need to adapt to the specific decisions being considered. In other words, accounting information systems need to be designed within an adaptive framework. Multi-divisional structure recognizes the unique environmental uncertainty facing different product market environment under a structure, it is highly important that top management possess the best predictive information model divisional environment. Sub-unit managers not only have a better understanding of local environments, but are also in a position to react more quickly to the information. The transmission of information from the superior down to lower cadre is suitable in a centralized environment which is subject to predictability. However vertical information flows also lead to information compression and time delays as information travels up the hierarchical level. Therefore, there is a need for a good system in place to ensure easy access to this information and the subsequent usage towards ensuring the formulation of a good decision for manufacturing industries.
Conceptual Review
Accounting information system and management of human resources
The importance of accounting information for beneficial decisions in respect of human resources management is aptly cited by Rapina [10] as ‘accounting information system is an integration of quality hardware, software, brain ware, telecommunication network and data base as well as quality of work and satisfaction of users’.
Information system of which accounting is a part is crucial tool for decision making in all aspect but most especially in manufacturing outfit as wrong decision is not easily reversible without dare consequence. Bodner et al. [11] affirms the nexus between accounting information system, governing policies and budget allocation. Overall performance of any organization stands to benefit through accounting information that ensure appropriate harnesses of the human resource within the organization.
Similarly, accounting information could provide a lead when an organization needs to expand, reduce, restructure its human ware, that is, it could provide needed information to arrive at rational, economical and most beneficial decision with far-reach consequence on human resource engagements.
Accounting information system and economic order quantity
The primary goal of manufacturing entity is to produce item of high quality with minimum possible input. Achieving this will directly lead to maximation of profit as it entails production with minimum cost. To achieve this, all elements of cost must be subjected to strict planning and control. However, among the three major elements of cost, it is found that cost of materials is responsible to over fifty per cent of total cost and this call for special attention of management. Accounting information system is the major means by which effective control could be exercised on this element. Furthermore, closer examinations of manufacturing firms’ financial statements are filled with the revelation of quantum of idle resources tied down on inventory with dare consequence on cash flows. This in view, there had been series of efforts to ensure inventory is maintained at most reasonable and economical level as much as possible. The scientific approach to the management of inventory is the application of economic order quantity which is an aspect of accounting information tool to aid short term decision making.
Farounbi [12], submit that the re order quantity when economically determined is known as economic order quantity while Akinola et al. [13], describe economic order quantity as the ordering quantity which minimizes the balance of cost between inventory holding costs and re-orders cost. The goal of minimizing cost of inventory without jeopardizing the quality of is what this is designed to guarantee. Shiro [14], corroborated this assertion that excessive inventory is an inefficient management of working capital and this is why accounting information will be of relieve to the management when it comes to making economic decision in respect of number of units of an item that must be ordered at a point in time which of course will be influenced with rate of consumption, delivery period, cost per order and the likes.
Accounting information and product development
The traditional view of marketing is that the firm makes something and sells it. However, making something for a sale is not as easy is not as easy as that as this requires a lot of planning. Making something that is already known and accepted by consumers may not require much than monitoring the performance of the product in the market but accounting information will be needed when new product is to be created. Whether a new product is acquired or developed accounting information will be required by the management to avoid new-product failure [15].
Manufacturing activities largely is a process of converting raw materials into goods that satisfy consumers’ need. Wood and Sangster [16] regard this as a supply chain. Accounting information is required at every stages of this value chain in the determination of cost and savings that will arise. Product development will be fraught with minimal rate of failure if and when accounting information is effective applied. There are series of cost/management accounting techniques that can provide planning information to assist in production, marketing/sales divisions of a manufacturing entity. For example, Cost Volume Profit (CVP) analysis can assist in the determination of unit price of a new product that will guarantee break even. It can also be of use to the management in the determination of how many units of a new product would the entity require to successfully market at a determined price that will be needed for breakeven position. This position is supported in Adeniyi [17] where he specifically mentions that break even chart is useful to plan the production and marketing of a company’s product.
Furthermore, marginal costing techniques are veritable accounting information for management in the decision making relating to either to introduce a new product or not. That is, management decision on whether the product will attract enough market acceptance that will guarantee the recovery of total cost of production with achieving a reasonable profit margin.
It is therefore not an exaggeration to assert that a successful marketing of a new product by manufacturing company will be influence on the use of accounting information by the various divisions that plan, execute and control the introduction of the product.
Empirical Review
In the financial management of the small enterprise investigated by Ismail [17] emphasized the positive correlation of the common belief that better financial information means better control and higher chance of success. This information is generated from the system (i.e. accounting system) by accountants in charge, is incorporated in the financial statements. Ratios (financial) analyzed from the financial statements constitute an element of this information. Therefore, there is need for proper incorporation of this system into manufacturing companies operation as it tends to make company operation difficult especially in areas like; performance evaluation, customer classification, possible future performance forecast, etc. A study conducted theoretically by Woodruff coupled with some statistical inferences, titled: The Systematic Access for Analyzing the Market Opportunities purports to demonstrate essentials of Product Demand Analysis-PDA. PDA is fundamental in the economic activity involving the definition and identification of feasible opportunities (investment) towards emerging the users (especially investors) in making realistic estimation of the profits. One of the vital recommendations for the study based on result obtained was to refrain users (especially investors) from investment in unproductive and unprofitable market.
Financial statements are well-structured and easily understood statements of a business enterprise, which helps to faithfully represent the overall condition (mostly financial) and state of operation of a business, necessary for possible estimation by its users for various strategic or short term based decision. Some of the basic statements as required by relevant standards include:
• Statement of Financial Position (formerly called Balance Sheet): This shows and emphasize basically on the asset, liabilities and equity of a particular business concern over a given period of time.
• Income statement; also referred as profit or loss statement, helps to show the realization of an entity’s income by duly consideration of the stocks (both opening and closing), goods purchased and relative sales made for the year. It is presented to inform the users better on the income generated at a particular time.
• Profit or Loss account; The company’s operation is given an analytical consideration here by comparing various relevant expenses made at a given period of time against the income realised to get the net income or profit for the year.
Statement of changes in equity; Explains the changes in the company earnings over the reporting period. It reports on a company's cash flow activities; particularly it’s operating, investing and financing activities. [18].
Several studies showed that the reduction of over investment could also be enhanced by a proper presentation of quality financial statements by companies. Agboola et al. [7] suggested that efforts should be made to incorporate qualitative information necessary for boosting the financial reporting of a business as it helps in increasing investment efficiency by encouraging investments in highly feasible projects, reducing investments in less feasible projects, and ensuring proper accountability of investors' wealth. In this regard, Biddle et al. [19] provide empirical evidence that high-quality financial reporting among firms reporting under U.S. GAAP increases investment efficiency. For a sample of private firms in emerging markets over the period 2002-2005. Chen et al. [20] also find that financial reporting quality positively affects investment efficiency. Collectively, the studies noted above suggest that an accounting choice (e.g. historical cost accounting with strict impairment rules) characterized by more timely loss recognition will reduce over-investment.
Previous studies had paid little attention to the influence of accounting on the management of inventory while there is dearth of attention on the use of accounting information in making rational decisions on introduction of new product to the market, and so it is on the employment of human resources in Nigeria. This study therefore bridged these gaps.
Justification of the Method of Estimation
A One sample t- test is considered appropriate for judging the significance of a sample mean or the significance of difference between the means of two samples in case of small sample(s) when population variance is not known (in which case we use variance of the sample as an estimate of the population variance). The basic idea of the test is to compare the average of the sample and the population, with an adjustment for the number of cases in the sample and the standard deviation of the average. This tells if the difference between two means is larger than would be expected by chance (i.e. statistically significant). It goes beyond just describing the numbers provided by data from a sample but seeks to draw conclusions about these numbers among populations
T-statistics
For analytical analysis the t-statistics is specified as:
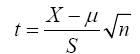
The statistic is described as Student’s t with n-1 degrees of freedom
Where, X = Sample mean
μ = population mean
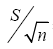 = standard error
= standard error
S = sample standard deviation,
n = number of sample
The sample size of one hundred and fifty staff of International Breweries Ilesha, Ola Oluwa Aina Wire Industry and Nigeria Machine Tools (all in Osun State, Nigeria) was randomly chosen for the study and structured questionnaire directly administered and collected which respondents’ distribution as shown in Table 1.
| Functional Level of Respondents | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top Management level | 38 | 25.3 | 25.3 | 25.3 |
| Middle Management level | 32 | 21.3 | 21.3 | 46.7 |
| Operational level | 80 | 53.3 | 53.3 | 100 |
| Total | 150 | 100 | 100 |
Table 1: Position held by the respondents.
The distributions clearly in support of reliability of generated data as about 47% of respondents were of management cadre, the levels directly involved in decision making. In addition, the questionnaire was reviewed by experts in managerial accounting, marketing and human resources to ensure that it appropriately solicits for relevant data needed for the study.
Data Presentation and Data Analysis
Descriptive analysis
Table 2 shows that 139 (92.7%) of the response collated in the course of the research admitted the fact that accounting information goes a long way in the determination of the amount or quantity of goods that should be ordered at a point in time and also insisted that unfavorable accounting information on a particular product would help in reducing ordered quantity is 139 (92.7%). Information generated from the accounting department helps in minimizing cost of ordered goods attracted the sympathy of 138 (92%) while 132 (88%) were of opinion that accounting information will reflect the effects of changes in the turnover of a product on the order of its inventory for production. Similarly, the number of respondents that agreed that accounting information generated on a particular line of product bring about a positive increase in the allocation of its resources is 135 (90%).
| Strongly Agree | Agree | Disagree | Strongly Disagree | Uncertain | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounting information generated goes a long way in determining the amount or quantity of good to be ordered for. | 68 (45.33) | 71 (47.33) | 6 (4) | 1 (0.67) | 4 (2.67) | 150 (100) |
| Unfavorable accounting information on a particular product would help in reducing its order quantity. | 63 (42) | 76 (50.67) | 6 (4) | 1 (0.67) | 4 (2.67) | 150 (100) |
| The information generated from the accounting department helps in minimizing cost involved in the ordering of goods. | 103 (68.67) | 35 (23.33) | 5 (3.33) | 3 (2) | 4 (2.67) | 150 (100) |
| The number of units of inventory required within a particular period of time can be shaped by accounting information. | 101 (67.33) | 36 (24) | 4 (2.67) | 4 (2.67) | 5 (3.33) | 150 (100) |
| Accounting information helps to reflect the effect of changes in the turnover of a product on the order of its inventory for production. | 97 (64.67) | 35 (23.33) | 12 (8) | 2 (1.33) | 4 (2.67) | 150 (100) |
| Lack of consideration of accounting information generated brings about uneconomical ordering of some goods. | 54 (36) | 83 (55.33) | 6 (4) | 2 (1.33) | 5 (3.33) | 150 (100) |
| The best quantity ordered at different level of discount is achieved by a good use of accounting information. | 52(34.67) | 86(57.33) | 8(5.33) | 2(1.33) | 2(1.33) | 150 (100) |
| Accounting information generated on a particular line of product brings about a possible increase in the allocation of its resources. | 54 (36) | 81 (54) | 11 (7.33) | 3 (2) | 1 (0.67) | 150 (100) |
Table 2: Accounting information and economic order quantity decision.
Table 3 provides that 52 (34.7%) are strongly agreed, 85 (56.7%) agreed, 11 (7.3%) disagreed and 2 (1.3%) strongly disagreed that optimum allocation of resources could be made by effective use of accounting information generated. The table also indicates that 84 (56.0%) of the respondents agreed that effective use of accounting information brings about a proper allocation of resources of competing activities 53 (35.3%) strongly agree, 11 (7.3%) of them disagreed while the remaining 2 (1.3%) strongly disagree. From the result,
| Strongly Agree | Agree | Disagree | Strongly Disagree | Uncertain | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimum allocation of resources could be made by effective use of accounting information generated. | 85 (56.67) | 11 (7.33) | 2 (1.33) | 0 (0) | 150 (100) | |
| Effective use of accounting information brings about a proper and good allocation of resources of competition activities. | 53 (35.33) | 84 (56) | 11 (7.33) | 2 (1.33) | 0 (0) | 150 (100) |
| Sub-optimal allocation of resources would be made when accounting information is not followed. | 45 (30) | 91 (60.67) | 10 (6.67) | 3 (2) | 1 (0.67) | 150 (100) |
| Good use of accounting information prevents wastage on the allocation of resources to different lines of product. | 89 (59.33) | 47 (31.33) | 10 (6.67) | 2 (1.33) | 2 (1.33) | 150 (100) |
| The use of limited resources to the best advantage among competing activities could be facilitated by proper use of accounting information. | 47 (31.33) | 89(59.33) | 11 (7.33) | 3 (2) | 0 (0) | 150 (100) |
| Accounting information provides a hint on what product or activities more resources should be committed to boost its turnover. | 95 (63.33) | 42 (28) | 8 (5.33) | 5 (3.33) | 0 (0) | 150 (100) |
Table 3: Accounting information and human resources management decision.
It can observed that 91 (60.7%) agreed that sub-optimal allocation of resources would be made when an accounting information is not followed. 45 (30.0%) strongly agreed, 10 (6.7%) disagreed, 3 (2.0%) strongly disagreed and 1 (0.7%) of them are uncertain about this statement.
Similarly, the descriptive result as shown in Table 4 confirms that 42 (28.0%) agreed that a good use of accounting information by management brings about introduction of new and better product in the market. 90 (60.0%) strongly agreed, 1 (0.7%) are uncertain, 2 (1.3%) strongly disagreed and 15 (10.0%) of them disagreed with the statement. Also, it shows that 85 (56.7%) of the respondents strongly agreed that a new product in the market is facilitated by an effective management decision through accounting information. The respondents that strongly agreed that the returns generated on a product shown by the accounting information go a long way in determining the continuity of the product are 46 (30.7%) while 83 (55.3%) agreed, 19 (12.7%) disagreed and the remaining 2 (1.3%). It is also noticeable from the result that 55(36.7%) agreed that lack of consideration of accounting information by the management brings about a late or no new product in the market. 80 (53.3%) strongly agreed, 10 (6.7%) disagreed and 5 (3.3%) strongly disagreed with the statement. Also, it can be deduced from this table that 46 (30.7%) are of the opinion that they agreed that the examination of increased demand in a particular product showed by accounting information may cause managers to introduce that product. 88 (58.7%) of them strongly agreed, 12 (8.0%) disagreed and the remaining 4 (2.7%) strongly disagreed.
| Strongly Agree | Agree | Disagree | Strongly Disagree | Uncertain | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A good use of accounting information by management brings about introduction of new and better product in the market. | 90 (60) | 42 (28) | 15 (10) | 2 (1.33) | 1 (0.67) | 150 (100) |
| A new product in the market is facilitated by an effective management decision through accounting information. | 85 (56.67) | 47 (31.33) | 12 (8) | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | 150 (100) |
| The returns generated on a product shown by the accounting information go a long way in determining the continuity of the product. | 46 (30.67) | 83( 55.33) | 19 (12.67) | 2 (1.33) | 0 (0) | 150 (100) |
| Lack of consideration of accounting information by the management brings about a late or no new product in the market. | 80 (53.33) | 55 (36.67) | 10 (6.67) | 5 (3.33) | 0 (0) | 150 (100) |
| The examination of increased demand in a particular product showed by accounting information may cause managers to introduce that product. | 88 (58.67) | 46 (30.67) | 12 (8) | 4 (2.67) | 0 (0) | 150 (100) |
| The introduction of a new product is geared by proper and efficient examination of accounting information by managers | 99 (66) | 37 (24.67) | 9 (6) | 3 (2) | 2 (1.33) | 150 (100) |
| The viability of a product showed in accounting information goes a long way in making manager hunt for introduction of the product. | 96 (64) | 41 (27.33) | 9 (6) | 2 (1.33) | 2 (1.33) | 150 (100) |
| The favorable cost-benefit analysis presented on a new product in the accounting information pre-empt managers interest in it. | 45 (30) | 88 (58.67) | 11 (7.33) | 5 (3.33) | 1 (0.67) | 150 (100) |
Table 4: Accounting information and marketing decision of new product.
Test of hypothesis
In hypothesis testing, statistical decisions are made to decide whether or not the population mean and the sample mean are different. One-sample t-test approach as applied in Royaee et al. [1] who was employed for the study to assess accounting information effectiveness in making decisions in manufacturing companies. In testing, the calculated value is compared with table or significant value. If the calculated value is greater than the table value significant value, then the null hypothesis is rejected, hence the alternative hypothesis is accepted. Other statistical tool employed in this study is descriptive (i.e. frequency count and percentages).
Hypothesis 1: The result of t-test conducted as shown in Table 5 shows that all items have an average value greater than the benchmark of 3.00 and a confidence level that is greater than 95% (i.e. p value<0.05) which denotes that they are statistically significant. By implication; there is a significant influence of accounting information on the economic order quantity decision in the selected manufacturing companies.
| SN | Item Details | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | t- Value | Sig. (2-tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accounting information generated goes a long way in determining the amount or quantity of good to be ordered for. | 150 | 4.32 | 0.81 | 65.03 | 0 |
| 2 | Unfavorable accounting information on a particular product would help in reducing its order quantity. | 150 | 4.29 | 0.81 | 65.18 | 0 |
| 3 | The information generated from the accounting department helps in minimizing cost involved in the ordering of goods. | 150 | 4.53 | 0.87 | 63.66 | 0 |
| 4 | The number of units of inventory required within a particular period of time can be shaped by accounting information. | 150 | 4.49 | 0.93 | 59.03 | 0 |
| 5 | Accounting information helps to reflect the effect of changes in the turnover of a product on the order of its inventory for production. | 150 | 4.46 | 0.9 | 60.55 | 0 |
| 6 | Lack of consideration of accounting information generated brings about uneconomical ordering of some goods. | 150 | 4.19 | 0.85 | 60.49 | 0 |
| 7 | The best quantity ordered at different level of discount is achieved by a good use of accounting information. | 150 | 4.23 | 0.72 | 71.41 | 0 |
| 8 | Accounting information generated on a particular line of product brings about a possible increase in the allocation of its resources. | 150 | 4.23 | 0.72 | 71.41 | 0 |
Table 5: There is no significant influence of accounting information on the economic order quantity decision of companies.
Hypothesis 2: Table 6 revealed that all items under consideration have average values greater than the benchmark of 3.00 and p-value less than 0.05. These provide evidence that there are statistically significant effects of accounting information on the human resources management decision. All the P-values suggested that the null hypothesis should be rejected; this implies that the alternative hypothesis (H1) is accepted.
| SN | Item Details | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | t- Value | Sig. (2-tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Optimum allocation of resources could be made by effective use of accounting information generated. | 150 | 4.25 | 0.64 | 80.71 | 0 |
| 2 | Effective use of accounting information brings about a proper and good allocation of resources of competitive activities. | 150 | 4.25 | 0.65 | 80.51 | 0 |
| 3 | Sub-optimal allocation of resources would be made when an accounting information is not followed | 150 | 4.17 | 0.69 | 73.79 | 0 |
| 4 | Good use of accounting information prevents wastage on the allocation of resources to different lines of product. | 150 | 4.46 | 0.79 | 69.04 | 0 |
| 5 | The use of limited resources to the best advantage among competing activities could be facilitated by proper use of accounting information. | 150 | 4.2 | 0.66 | 78.49 | 0 |
| 6 | Accounting information provides an hint on what product or activities more resources should be committed to boost its turnover. | 150 | 4.51 | 0.75 | 73.85 | 0 |
Table 6: There is no significant effect of accounting information on human resource management decision of companies.
Hypothesis 3: All the items in the Table 7 have an arithmetic means greater than 4.00 and p-value less than 0.05 and this implies that accounting information significantly affects the introduction of new products decisions in the selected manufacturing companies. On the premises that all the items have p<0.05, the study therefore established that there is significant influence of accounting information on marketing of new product decision
| SN | Item Details | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | t-Value | Sig. (2-tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A good use of accounting information by management brings about introduction of new and better product in the market. | 150 | 4.45 | 0.78 | 69.73 | 0 |
| 2 | A new product in the market is facilitated by an effective management decision through accounting information | 150 | 4.39 | 0.87 | 61.54 | 0 |
| 3 | The returns generated on a product shown by the accounting information go a long way in determining the continuity of the product. | 150 | 4.15 | 0.68 | 74.49 | 0 |
| 4 | Lack of consideration of accounting information by the management brings about a late or no new product in the market. | 150 | 4.4 | 0.76 | 70.93 | 0 |
| 5 | The examination of increased demand in a particular product showed by accounting information may cause managers to introduce that product | 150 | 4.45 | 0.76 | 72.14 | 0 |
| 6 | The introduction of a new product is geared by proper and efficient examination of accounting by information managers. | 150 | 4.52 | 0.81 | 68.46 | 0 |
| 7 | The viability of a product showed in accounting information goes a long way in making manager hunt for introduction of the product. | 150 | 4.51 | 0.78 | 70.55 | 0 |
| 8 | The favorable cost-benefit analysis presented on a new product in the accounting information pre-empt managers interest in it. | 150 | 4.14 | 0.74 | 68.32 | 0 |
Table 7: There is no significant relationship between accounting information and marketing of new product decision of companies.
Summary of findings
The results of analyses show that accounting information has significant impact on the economic order quantity decision of the manufacturing companies. This means that an effective use of accounting information by the company will have positive impact on their economic order quantity decision and this align with Siyanbola [21] that also confirmed that efficient accounting information plays a central role in management decision making.
Furthermore, the study revealed that there is a significant effect of accounting information on the human resource management decision of the companies which implies that accounting information adopted by companies affect the management of resources whether there is need to allocate substantial human resources into a particular product line or not and this aligned with the finding in Ullah et al. [22].
Conclusion
The objectives of the firm differs from one organization to another hence the research concluded that the application of accounting information makes the difference between failed companies, on one side and the successful one on the other side. For the improvement in the application of accounting information to be sustained, adequate understanding of the difficulty in the application of accounting information is very essential. If this is applied as at when due failure in business both private and public sectors will be highly minimized. Accounting information on decision making process has helped in the proper allocation of resource such as material, money, machinery and human.
The reliance on management accounting information will go a long way to assist in decision making involving planning and control of inventory, engagement of human resource to drive the success story of manufacturing outfits and more importantly in development and introduction of new product into the market.
Robust and effective decisions will enhance service delivery of manufacturing companies as much as to the promotion of corporate survival in the face of growing competitive environments in which manufacturing companies operates.
Recommendations
Accounting information is very essential to the users’ for their development, especially when it extends to decision making. In view of the above, the following recommendations were deemed necessary.
The use of accounting information to arrive at optimal inventory management can no longer be overemphasis as the studies established a strong link between economic order quantity decision hence it is advice that management should ensure decisions are supported with data generated through the accounting information system and jettison the practice of rule of thumb when it comes to inventory decisions
Employment and deployment of human resources should be done relying on data through accounting information system as the study confirmed that there is strongly relationship accounting information system and human resources management. Manufacturing organization should increase the use of accounting information in marketing decisions in bringing in new product into the market, increasing sales volume and in taking better marketing strategy.
References
- Royaee R, Salehi A, Aseman, HS. Does accounting play a significant role in managerial decisions? Res J Bus Manage Acc. 2012;4:57-63.
- Law J. Dictionary of business and management, 6th ed. London, Oxford University Press. 2009.
- Freeman RE. Strategic Management; A Stakeholder Approach. Boston, Pitman. 1984.
- Wood F, Sangster A. Business accounting, Book 1, 12th ed. Edinburg Gate, Pearson Education Limited. 2012.
- Brennan MJ, Copeland TE. Stock splits, stock prices, and transaction costs. J Financ Econ. 1988;22:83-101.
- Fama EF, Fisher L, Jensen M, et al., 1969. Retrospective comments. SSRN Electronic Journal. 2013.
- Oyerogba EO, Solomon AZ, Olaleye MO. Cost management practices and firm’s performance of manufacturing organizations. Int J Finance Econ. 2014;6:234-239.
- Arthurs JD, Busenitz LW, Hoskisson RE, et al. Signaling and initial public offerings: The case and the impact of the lockup period. J Bus Venturing. 2009;4:360-372.
- Adesina OT, Ikhu Omoregbe S, Aboaba KO. Accounting information and profit planning: The case of Nigeria listed manufacturing companies. Europ J Agri Forest Res 2015;4: 86-97.