Research Article - Journal of Industrial and Environmental Chemistry (2023) Volume 7, Issue 2
Artificial rainmaking in large scale by laser system onboard aircraft
SK Chopkar* and DK. Chakrabarty
Innovative Rainmaking Research Association (IRRA) Sevagram- 442102, Maharashtra, India
- Corresponding Author:
- Chakrabarty
Innovative Rainmaking Research Association (IRRA) Sevagram- 442102
Maharashtra, India
E-mail: skc.arr@rediffmail.com
Received: 06-March-2023, Manuscript No. AAIEC-23-91879; Editor assigned: 08-March-2023, PreQC No. AAIEC-23-91879(PQ); Reviewed: 16-March-2023, QC No AAIEC-23-91879; Published: 23-March-2023, DOI:10.35841/aaiec-7.2.140
Citation: Chakrabarty DK, Chopkar SK. Artificial rainmaking in large scale by laser system onboard aircraft. J Ind Environ Chem. 2023;7(2):140
Abstract
A number of scientific and practical tests have been conducted in cloud chambers and in the atmosphere to prove this hypothesis, that “Laser can induce condensation and water drops can be formed in laboratory cloud chambers as well as in the atmosphere”. Innovative Rainmaking technology is scientifically and practically proven in Laboratory clouds chamber and in the atmosphere. A laser beam has to be shot into the cloud region of the atmosphere to create high temperature. This high temperature will break the bonds of N2 and O2 molecules of the atmosphere and produce N and O atoms. These atoms will be in excited state (N*, O*). They are very unstable and come to stable ground state through endothermic reactions by sucking heat from the cloud region. As a result, temperature of the cloud region decreases, condensation takes place, seeds are created, and it rains. IRRA Scientist to start with have suggested a laser system of following specification is suggested to create artificial rain: 1012watt, 800nm, 500mJ, 120fs and 10Hz by Air craft for artificial rain in large scale, direct Laser shot into the cloud region of the atmosphere.
Keywords
Artificial rain, Atmospheric cloud, Condensation, Endothermic reactions, Laser system, Precipitation, Raindrops, Natural Seeding, Rainfall.
Introduction
Several attempts have been made by various workers to create artificial rain by laser. Golde (1977) from a number of radar observations has reported that intense precipitation is not even present in the clouds before the first discharge but develops abruptly in the same region after discharge from which the lightning flashes originate. Carls and Brock (1987) heated the atmosphere by a laser pulse up to 1600 to 2800K and observed water droplet formation. They predicted that high temperature causes ionization of N2 and O2 and, when this ionized air is subjected to more radiation, avalanche breakdown of air can occur. Braun et al. (1995) have observed laser induced condensation and water drops formation by shooting selfchanneling of high- peak power femtosecond laser pulses in the air. Yoshihara et al. (2007) have shown that the pulsed UV-laser irradiation of ambient air induces formation of water droplets or small ice particles in the laboratory. They also observed that [O] formed in this process quickly reacts with O2 molecules to form O3. Rohwetter et al. (2010) have shown that ionized filament, generated by ultra-short wave laser pulses induce water-cloud condensation in the subsaturated atmosphere in the altitude region between 45m and 75m. A team, called terra-mobile-group (TMG), consisting of scientists from Switzerland, Germany and France, have been trying to create artificial rain by laser (Kasparian et al.2000; 2003; Mejean et al. 2006; Rohetteret al. 2010; Kasparian et al. 2012). They have done simulation experiment in laboratory cloud chamber and have observed condensation and water drops formation. They also succeeded in producing tiny water particles in moderately humid air in an altitude of 45 to 75m of the atmosphere by terawatt mobile laser. But the droplets were about a hundred times too small to fall as raindrop; instead, they remained suspended in the air. The team feels that it is feasible to get larger droplets if the power of laser is increased to petawatt (1015watts) or exawatt(1018watts). They further say that the effectiveness of this method is much easier to gauge than traditional cloud-seeding techniques and that it could provide to be a practical means of triggering rainfall”. (Search Google as ‘Laser makes rain, heavily’(2010) [1-2]. A group of Scientists from Florida University also observed water drops formation by high power laser shooting experiment. It appears from the above that laser has not yet succeeded in producing artificial rain. In this paper, a novel method is described to create artificial rain by laser system through Aircraft in the atmosphere.
How Will Laser Create Artificial Rain? Theory
For creation of rain, according to well established meteorology theory (can be found in any textbook of meteorology), steps are the following:
First (i) creation of low temperature →then (ii) condensation then (iii) seed (CCN) formation
→then (iv) tiny water drop formation and rain occur in the atmosphere.
The present methodology is to send laser pulse to the cloud region of the atmosphere to create high temperature. This high temperature will break the bonds of O2 and N2 as follows:
N2 : N ≡ N →N* + N ---- (1)
O2 : O = O → O* + O (2)
In this process N and O will be created in excited state (N*, O*). These excited N* and O* are very unstable and immediately come to the ground state through following reactions.
N* + O2→NO + O ΔH (43.2kcal/mol) (3)
O* + O2 + M → O3 + M ΔH (67.7kcal/mol) (4)
The occurrence of reactions 3 and 4 and formation of NO and O3 have confirmation from NASA laboratory experiments [Sanders et al. 2003]. Formation of O3 and NO, after laser shot, has been observed in laser experiment in atmosphere (Petit et al. 2010). The reactions 3 and 4 are endothermic and therefore, they need heat energy (amount mentioned in brackets) which is absorbed from the cloud region. As a result, temperature of the cloud region falls (first step of rain formation is achieved and then other steps follow), condensation takes place, seeds (CCN) will be formed, and tiny water drops will be created. These tiny water drops may act as natural seeds to form another sets of rain drops. This chain process will result in rainfall. Ozone and Nitric oxide, O3 and NO (formed in reactions 3 and 4) will undergo further reaction to form HNO3 particles other nitrogen compounds, which will bind water molecules together to create water droplets. These water droplets again will act as natural seeds to form another sets of rain drops [3]. In the atmosphere, due to turbulence, small water drops coalesce and form big rain drops. In addition, ions N2+and O2+ and electrons formed by cosmic rays can create complex hydrated heavy positive and negative ions... HNO3-. (H2O)n (where the value of n could be as large as 50) which can also act as seed to create rain. In short, to create artificial rain by laser, endothermic reactions are to be generated in the cloud region. It has-been shown earlier how much heat energy is absorbed by endothermic reactions from atmospheric clouds (Chopkar 1993a,b; Chopkar and Chakrabarty 2008; Chakrabarty et al. 2010; Chopkar et al. 2010) [4]. The energy required to break bonds of 1 molecule of N2 and 1 molecule of O2, = 2.25x10-18 Joule. A laser pulse of energy 500mJ can dissociate a column of N2 and O2 containing (~0.5/2.25-18) ~ 1017molecules which is much higher than the density in the atmosphere. Laser can be operated from ground as well as from an aircraft. In former case, laser pulse has to propagate to a height of ~1km (cloud height) from the ground. There will be attenuation of energy in this propagation. Kasparian et al. (2012) experimented with terawatt laser from the ground and observed tiny raindrops in an altitude of 45m to 75m of the atmosphere. To create large water droplets at higher altitudes, the group feels that laser power has to be peta-watt (1015watt) or hexa-watt (1018watt). If laser is operated from aircraft then attenuation of energy will be less. In that case, laser power can reach the cloud region without much attenuation. So, “Rainmaking Technology by Laser System through Aircraft initiating Endothermic Reactions similar to Natural Lightning Phenomena for Artificial Rainmaking in large scale in the Atmosphere”[5,6].
It can also cover large area and can move to any place. Turbulence created by the aircraft in the atmosphere can also create small water drops which would collide with each other and form big rain drops.
Condensation is the Basic Need for Water Drops Formation
IRRA Scientist Group has successfully shown by laboratory experiment that ‘condensation is the basic need for water drop formation’. That condensation is the basic need for water drop formation can be understood by taking two glasses, one filled with normal water and another with ice pieces. After sometime one can observe water droplets on the outer surface of the glass which contains ice but not in the other. This is due to the condensation process that occurs around the ice glass [7]. So, IRRA Scientist Group, proposed a laser system for this research project, to create artificial lightning by initiation of endothermic reactions, similar to natural lightning phenomena, for artificial rainmaking. As a result of these reactions, temperature falls, condensation takes place, seeding occurs and it rains in an analogous way rain is created by lightning. This process has been practically proved in the laboratory and atmosphere as “production of ozone and nitrogen oxides by laser filamentation” [8]. A number of scientific and practical tests have been conducted in cloud chambers and in the atmosphere to prove this hypothesis, as “Laser induce condensation and water drops formation by Laser shooting in the laboratory cloud chambers as well as in the atmosphere”.
Now the question arises that what are the conditions required for condensation. This means that, only and only, endothermic reactions are responsible for condensations, which also produces NO (Nitrogen Oxides) and O3 (Ozone) after shooting laser beams triggering endothermic reactions, condensation and precipitation. These tiny water drops act as a natural seeding process, due to acceleration and tribulation by wind force in the atmosphere, to form another set of raindrops with heavy rainfall as lightning rain. Endothermic reactions are responsible for condensation. Condensation is the basic need for water drop formation as above laboratory experiment, “Condensation is the Basic Need for Water Drops Formation”. This novel Rainmaking Technology can be used for white, warm clouds too which get converted into black rainy clouds for rain enhancement. As well as, water drops formation by high power Laser shooting, “Laser makes rain” [9].
The IRRA scientist Group has already demonstrated “Innovative Rainmaking Technology” in the Laboratory cloud’s chamber successfully, and results have been published in “Indian Journal of Science & Technology”, http://indjst. org, vol.1, No.6 (2008).
Now, the project proposal, the design of the laser system, the Budget estimate, and the work plan are ready with IRRA Scientist Group, India. IRRA Scientist is ready for demonstration and collaboration with the Government for funding purposes for project proposal on “An Innovative Rainmaking Technology using Laser system from Aircraft to form raindrops acting as the natural seeding process due to initiation of Endothermic Reactions, for rain enhancement in large scale in the atmosphere”.
In this experiment, femto-second–terawatt laser creates artificial lightning in the atmospheric clouds regions by Air craft. These white warm clouds are converted into black rainy clouds with natural seeding for rain enhancement in the atmosphere.
A laser pulse will be sent to the cloud to initiate endothermic reactions which will create lightning phenomena, as in nature, mentioned above. For example, a German-French group has used a femtosecond–terawatt laser to obtain “Laser-assisted water condensations in the atmosphere’’. They have succeeded in obtaining raindrops from an altitude of 45m to 75m of the atmosphere [10].
This novel Rainmaking Technology can be used for white, warm clouds too which get converted into black rainy clouds for rain enhancement.
*As well as, water drops formation by high power Laser shooting. “Laser makes rain” by Florida University, Scientist experimentally observed.
*As per report, a group of European scientists working on artificial rain said in 2010, “Firing extremely powerful laser pulses through humid air can stimulate the formation of clouds. They say that the effectiveness of this method is much easier to gauge than traditional cloud- seeding techniques and that it could provide to be a practical means of triggering rainfall” [11]. (Search Google as ‘Laser makes rain, heavily’2010). In an ancient Indian religious book, Vedshastra there is a mention “Fire arrows are sent towards the atmospheric clouds which is responsible for immediate rainfall”
Our system could be a terawatt femtosecond Ti:sapphire pulse laser. Its fundamental wavelength could be ~800nm. The pulse will have energy of ~500mJ, 120fs and repetition frequency of 10Hz. The laser pulse has to propagate with almost high peak intensity in atmospheric clouds. It works when more than 65% humidity is present in the atmosphere. Our findings could be used by scientists and engineers to create artificial rain. The results could be of immense benefit to human being.
Methodology for Rainmaking
A laser pulse is sent to cloud to initiate endothermic reactions which will create lightning phenomena as in nature, mentioned above.. For example, a German- French group has used femtosecond–terawatt laser to obtain“Laser- assisted water condensations in the atmosphere’’. They have succeeded in obtaining raindrops from an altitude of 45 to 75m of the atmosphere. Our system could be a terawatt femtosecond Ti:sapphire pulse laser. Its fundamental wavelength could be ~800nm. The pulse will have energy ~500mJ, 120fs and repetition frequency of 10Hz. The laser pulse has to propagate with almost high peak intensity over a distance of ~1km [12]. This laser system can be operated from ground as well as from aircraft. But there are some advantages for operating this system from the aircraft. Some of them are as follows:
A) Laser system cannot be used from ground level for artificial rainmaking because laser intensity with high power cannot reach a height of ~1km in the atmosphere due to loss of energy in travelling.
B) If laser system is used from ground level, then natural lightning may come to ground through laser beam and damage laser instruments and may harm workers who are working there.
C) If laser system is used from ground level, then it cannot cover large area as in aircraft system as aircraft laser can cover more than 200 km2 area in one time.
D) Laser system from ground level cannot move easily from one place to another place but aircraft laser system can move to any place easily.
E) Aircrafts, femtosecond-terawatt laser and other equipments are easily available in market.
F) Acceleration and turbulence created by the aircraft in the atmosphere creates small water drops which collide with each other and form big rain drops.
Therefore, IRRA Scientist Group, proposes femtosecond– terawatt laser system of specification 1012watt, 800nm, 500mJ, 120fs and 10Hz for this research project- “To create artificial lightning by laser system on board Aircraft which initiation endothermic reaction, similar as Natural Lightning Phenomena for artificial rainmaking, on large scale in the atmosphere” (as shown in Fif.No.1).
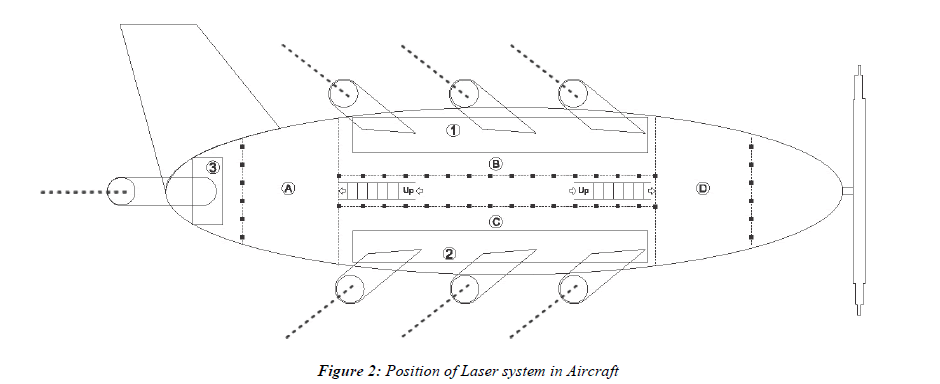
As shown in figure No.2, “Inner Design of Aircraft with Laser system” in Fig.No.2: Position of Laser system in Aircraft.
* In the figure, on first floor, height 9’ , the parts shown in (1),(2) and (3) are high power Laser release system which creates multiple artificial Lightning in the atmosphere, directly in upper clouds by Laser system
* In the figure, on second floor, height 7’6”, the parts shown in (A),(B),(C) and (D) with stair case are high power generation system for high power Laser system.
In Aircraft, there are two compartments. In the 1st Floor height 9’ Laser instrument is installed as shown in Fig.No.2 ,and 2nd Floor height 7’ 6” high power energy supply unit is installed as shown Fig.No.2 .
For this experiment, seven terawatt femtosecond Ti:sapphire Laser instrument is to be installed inside Air craft as shown in figure No.2.
Aircrafts equipped with laser system will be used in this operation as shown in Fig.No.2. In the aircraft, seven Laser instruments shall be installed, three right side (as shown in part-1) and 3 left side(as shown in part-2) ,one back side of Aircraft . Aircraft will release seven laser beams in the atmospheric clouds. They will cover more than 200Km2 area. Speed of aircraft will be slower up to 100km/h. In aircraft there shall be an instrument by which we can measure the atmospheric parameters.
Artificial rainmaking by laser system through aircraft
“Innovative Rainmaking Technology” is scientifically and practically proved in Laboratory clouds chamber as well as in the atmosphere.
This laser system can be operated from Air craft for artificial rain in large scale, direct Laser shot into the cloud region of the atmosphere, as shown in figures No.1 (No loss of energy in Laser trawling). In this figure, terawatt femtosecond Ti:sapphire pulse laser energy is used for creating artificial lightning in the upper atmospheric clouds for initiation of endothermic reactions, lot of heat energy absorbs from surrounding atmospheric clouds, condensations take place, water drops formations in the atmosphere. Due to accelerations & turbulences by wind forces in the atmosphere, these water drops, it’s used as natural seeding process, to form another sets of raindrops, chain process occurs for rain enhancement in the atmosphere [13].
Air craft released at a time 7 Laser pulse in upper atmospheric clouds, direct Laser shot into the cloud region of the atmosphere which creates artificial lightning in the atmospheric clouds.
When the upper atmosphere is cloudy and more than 65% humidity is present in the atmosphere, the experiment can be started in the atmosphere.
We have to measure atmospheric parameters such as humidity, temperature, pressure, wind velocity, wind direction, etc. on ground level as well as in the upper level of atmosphere . For this purpose, a separate unit/department should be made as “Measuring & Maintains Department”. After the success of experiment, all related data, have to be put in computer, for analysis and conclusion, with fixed perfect Laser design for maximum rainmaking in the atmosphere.
In this way “Innovative Rainmaking Technology using for Artificial Rainmaking in large scale by Laser system through Air craft in the atmosphere”, can be used for Green revolution in the whole world for all human beings.
Figure 2: Position of Laser system in Aircraft.
Note: * In figure No. 2, on first floor, height 9’, shown parts (1), (2) and (3) are high power Laser release system which creates multiple artificial Lightning in the upper atmospheric clouds directly by Laser system ……
* In figure No.2, on second floor, height 7’ 6”, shown parts (A),(B),(C) and (D) with stair case are high power generation system for high power Laser system, with railing for open space as shown square dots …..
Discussion
Innovative Rainmaking Technology is scientifically and practically proved as “Laser induces condensation and water drops formation in Laboratory cloud’s chamber as well as in the atmosphere”.
However, according to Kasparian group, a laser pulse shot in the atmosphere ionizes N2 and O2
N2 + hν → N2+ + e- (7)
O2 + hν →O2+ + e- (8)
They have observed lightning phenomenon in the laboratory cloud chamber as “Laser induced condensation and water drops formation in the laboratory cloud chamber by Femtosecond – Terawatt mobile laser system”. Kasparian (2012) group says that it is the ionized species N2+ and O2+ which produce rain. But these two species are of micro size which cannot act as seeding agents. Also N2+ and O2+ radicals are not observed by Kasparian group in laser filamentation experiments but production of O3 and NO has been observed by them in laser filamentation experiments [14]. Experiments of Kasparian group finds condensation and water drop formation and they say in their ionization theory that N2+ and O2+ act as seeding agent. They also say “Mechanism of laser–induced condensation involves photo dissociation, in which photons break down atmospheric compounds in the atmosphere”. This process produces Ozone and Nitrogen oxides, which lead to the formation of Nitric acid particles that bind water molecules together to create water droplets.” But there is no seeding and condensation and water drop formation is not due to seeding. Small water drops formed by laser in the laboratory cloud chamber are due only to endothermic reactions (cooling) and this is obvious. In the atmosphere, due to acceleration and turbulence, these small sized water drops coalesce to form big rain drops. These rain drops act as a natural seeding process to form different sets of rain drops; this chain process continues with heavy rainfall.
Calculation for the energy required for dissociation is almost half of that required for ionization The energy of a laser beam of wavelength λ is hν (ν = 1/λ and h is Planck’s constant). We will shoot laser pulse in the atmosphere and dissociate (break bonds of) N2 and O2 as follows:
N2 + hν → N* + N (9)
O2 + hν → O* + O (10)
Bond energy of N2 = 226 kcal/mole.
1 cal = 4.184 Joule, Avogadro number = 6x1023
Therefore energy required to break 1 molecule of N2 = 226x103x4.184/ (6x1023) = 1.58x10-18 Jou Bond energy of O2 = 96 kcal/mole.
Therefore energy required to break 1 molecule of O2 = 96x103x4.184/ (6x1023) = 0.67x10-18 Joul So the total energy required for breaking 1 molecule of N2 and 1 molecule of O2 will be (1.58x10-18 + 0.67x10-18) = 2.25x10-18 Joule.
When a laser pulse is shot in the atmosphere, it may ionize N2 and O2 as follows:
N2 + hν → N2+ + e (3)
O2 + hν → O2+ + e (4)
Ionizing potential of N2 = 15.58 ev = 2.49x10-18Joule
Ionizing potential of O2 = 12.2 ev = 1.95x10-18Joule
So the total energy required ionizing 1 molecule of N2 and 1 molecule of O2 is 2.49x10-18Joule
+1.95x10-18 Joule = 4.44x10-18Joule.
The above calculation shows that the energy required dissociating 1 molecule of N2 and 1molecule of O2 is about half of that required to ionize them.
The energy required for dissociation is almost half of that required for ionization. That means energy is first used up for dissociation, then the remaining energy (which may not be sufficient for ionization of N2 and O2) is delivered for ionization of N2 and O2. Hence dissociation takes place and not ionization. The Kasparian group does not talk about dissociation. It is not only near the IR laser system, Yoshihara, et al. (2007), have discussed in their paper the possibility of creating artificial rain by using UV lasers. Our methodology is to send laser pulses to cloud regions to break bonds of O2 and N2 (by reactions 1 and 2), create endothermic reactions and condensation (by reactions 3 and 4) and produce rain in the similar way as in lightning. There is attenuation of energy in operating the laser through Aircraft [15].
Kasparian's group suggests an increase of laser power to petawatt (1015watt) or exawatt (1018 watt) to create large water droplets. We will operate from an aircraft in the same way as spraying chemicals from Aircraft. A laser pulse of energy 500mJ is capable of dissociating a column of N2 and O2 containing (~0.5/2.25-18) ~10-17molecules which is much higher than the density in the atmosphere.
Additional Uses
This method can be used for rain harvesting by “rain drain”. When huge clouds are present above a lake or dam, a laser beam can be shot into the cloud region; then with blast of clouds heavy rainfall will occur to fill the lake or dam for future use of water. This method can also be used to reduce pollution of the atmosphere by spraying artificial rain on the polluted city. Another use of this method is to stop excess rainfall. Low intensity laser pulse shot into the cloud region will evaporate the clouds from the excess rainfall area. This method can also be used to drive away the rain cloud from the region where rain is not needed.
Conclusion
Innovative Rainmaking technology is scientifically and practically proven, as “Laser induces condensation and water drops formation by Laser shooting in the laboratory cloud chambers as well as in the atmosphere”.
Now, the project proposal, the design of the laser system, the Budget estimate, and the work plan are ready with IRRA Scientist Group, India. IRRA Scientist is ready for demonstration and collaboration with the Government for funding purposes for project proposal on “An Innovative Rainmaking Technology using Laser system by Air craft to form raindrops acting as the natural seeding process due to initiation of Endothermic Reactions, for rain enhancement in large scale in the atmosphere” resulting techniques could be of inestimable value.
It is shown in this article that by initiating endothermic reactions in the cloud region of the atmosphere by a laser, artificial rain can be created. Laser may have the following specification: 1012watt, 800nm, 500mJ, 120fs and 10Hz for operation by Air craft. This method is economical (one time investment), harmless, eco-friendly and can be switched on and off when desired. It can be used at any place and at any time, for Green revolution in the whole world for all human beings.
Acknowledgement
We express our sincere thanks to several scientists of RTM Nagpur University. We also thank Prof. B. Padmanabha Murthy of J. N. University, New Delhi; Prof. B Korgaokar, University of Pune, Pune; Dr. G.L. Agrawal of National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur; Dr. R.M.Kharate, Shri Gajanan Maharaj Engineering & Research Institute,Shegao; Prof. Jzsef Dr.Steier, Dhakala Marocco, Dr. Umesh Kushetra,J.N.University,New Delhi; Dr. Nitin Saraf, B.D.Engineering college, Sevagram; Dr.K.R.Gangakhedkar, P.N.College,Nanded; Dr. A. K. Nath of IIT, Kharagpur.
References
- Braun A, Korn G, Liu X. et al. Self-channeling of high-peak power femtosecond laser pulses in air. Opt. Lett. 1995;20:73-75.
- Carls, JC, Brock, JR. Explosion of a water droplet by pulsed laser heating. Aerosol Sci. Technol., 1987;7: 79-90.
- Chopkar, SK. Chakrabarty DK. Artificial rainmaking system in a way of natural phenomena. Indian J. Sci. Technol, 2008;1:1-5.
- Chakrabarty, DK, Chopkar SK, Purkait NN. Femtosecond terawatt laser system to produce artificial rain presented at 4th international conference on computer and devices for communication, CODEC 2009 at Kolkata in December 2009 and published in IEEE X-plore digital library, INSPEC Accession No. 11136783, Print ISBN 978-1-4244507329, February 2010.
- Chopkar SK. Effect of endothermic reactions associated with lightning on atmospheric chemistry. Indian J. Radio Space Phys.1993;22:128-131.
- Chopkar, SK. American Meteorological Society in Meteorological & Geo-astrophysical Abstracts. 1993;44.
- Chopkar SK., Chakrabarty DK, Sonbawane SM, et al. Innovative rainmaking technology for artificial rainmaking in large scale by laser system onboard air craft. International J. of Meteorology. 2010;35(355): 363-370.
- Kasparian J, Sauerbrey R., Chin S.L. The critical laser intensity of self-guided light filaments in air. Appl. Phys. 2000; 877-879.
- Kasparian J, Rodriguez M., Mejean, G. et al. White-light filaments for atmospheric analysis. Science, 301, 61-64, 2003.
- Kasparian, J, Rohwetter, P, Wöste L, et al. Laser-assisted water condensation in the atmosphere: a step towards modulating precipitation. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics.2012; 45(29).
- Mejean G, Ackermann R, Kasparian J, et al. Improved laser triggering and guiding of megavolt discharges with dual fs-ns pulses. App. Phys. Letts. 2006; 88: 021101.
- Petit Y, Henin S, Kasparian J. et al. Production of ozone and nitrogen oxides by laser filamentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010; 97, 021108.
- Rohwetter P, Kasparian J, Stelmaszczyk K. et al. Laser-induced water condensation in air, doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.115, 2010.
- Sander SP, Friedl RR, Golden, DM. et al. Chemical kinetics and photo-chemical data for use in atmospheric studies. NASA JPL publication. 2003;02-25.
- Yoshihara K, Takatori Y, Miyazaki K. et al. Ultraviolet light-induced water- droplet formation from wet ambient air. 2007; Proc. Jpn. Acad. Sci. B 83, 320.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref