Clinical Image - Annals of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery (2018) Volume 1, Issue 1
Unusual aspiration of foreign body in adults.
Reza Afghani1* and Mahmoud Khandashpour Ghomi2
1Thoracic Surgeon, Department of Surgery, Azar Hospital, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran
2Pulmonologist, Bronchoscopy Ward, Sayad Shirazi Hospital, Golestan University of Medical Science, Gorgan, Iran
- *Corresponding Author:
- Reza Afghani
Department of Surgery
Golestan University of Medical Sciences
Gorgan, Iran
Tel: +98 17 3225 3500
E-mail: af_med75@yahoo.com
Accepted date: October 16, 2017
Citation: Afghani R, Ghomi MK. Unusual aspiration of foreign body in adults. Ann Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017;1(1):8-10.
DOI: 10.35841/cardiovascular-surgery.1.1.8-10
Visit for more related articles at Annals of Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeryAbstract
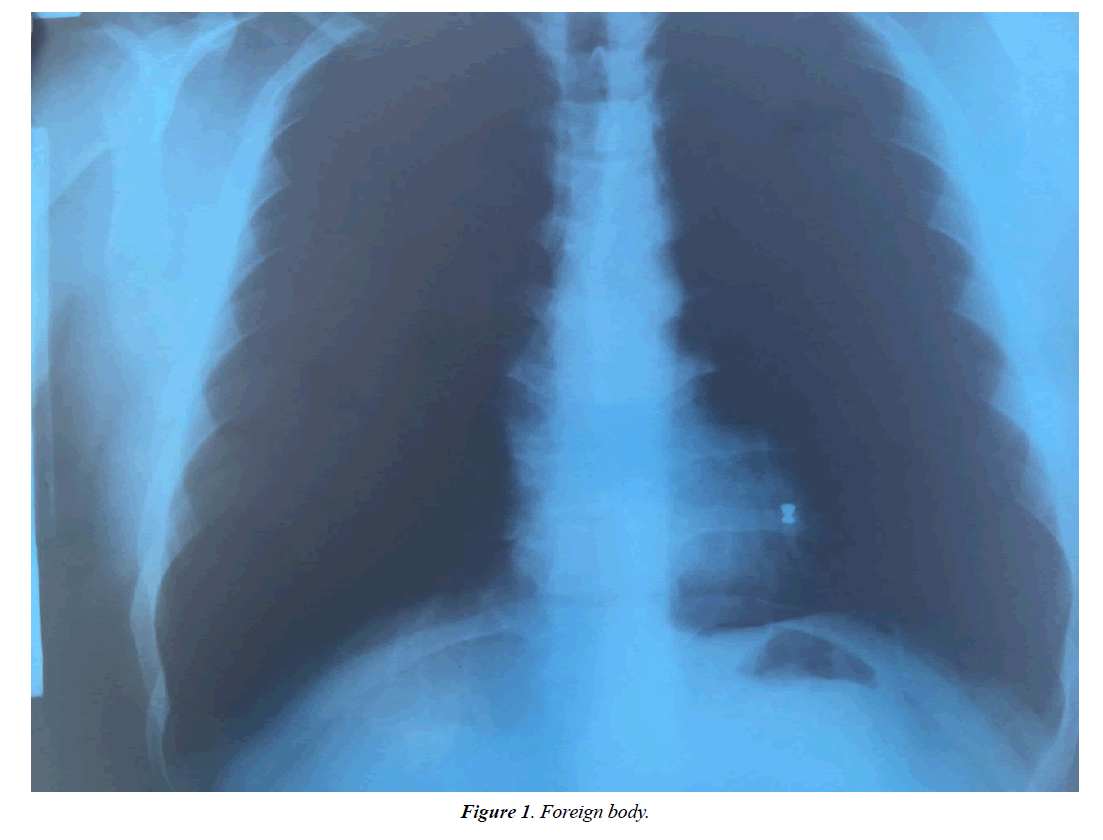
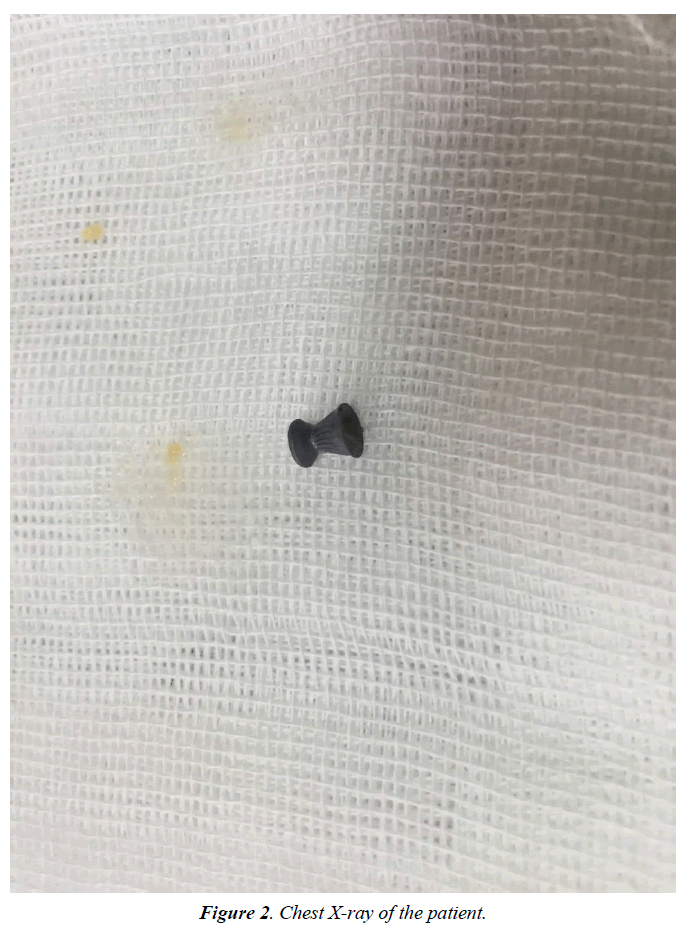
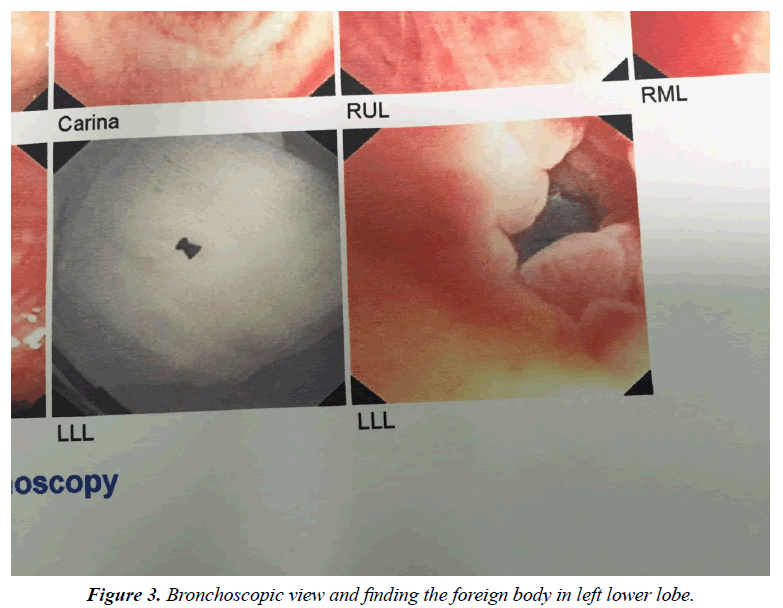
Aspiration of foreign body can occur in children and adults. Children swallow objects due to their curiosity and are prone to aspiration. However in adults there are different risk factors for aspiration; such as alcohol consumption, addiction, drug consumption, senility, seizure, trauma, mental retardation, and artificial dentures [1]. In some cases, it may happen accidentally, and risk factors are not involved. In this particular case, air gun bullet has been swallowed (Figure 1). The shooter had put a bullet in his mouth in order to reload his gun and shoot rapidly; then swallowing and aspiration happened. In this case, because the foreign body is opaque, chest X-ray can be helpful for diagnosis (Figure 2). The alternative way to diagnose is fiberoptic bronchoscopy; which is sometimes considered a therapeutic strategy (Figure 3). Foreign body aspiration in tracheobronchial tree requires immediate diagnosis and removal; because the ignored objects may result in complications like infection, abscess, empyema, and haemoptysis or even bronchopleural fistula [2]. Therapeutic options to remove aspirated foreign bodies from the respiratory tract are carried out through fiberoptic and rigid bronchoscope [3]. In cases of immediate removal of the foreign body, the outcome will be excellent; and there will be no specific complication and sequel. In some rare cases, surgery is needed to remove the foreign body; however, surgery is mostly required in situations with late diagnosis and occurrence of complications.
Clinical Image
Aspiration of foreign body can occur in children and adults. Children swallow objects due to their curiosity and are prone to aspiration. However in adults there are different risk factors for aspiration; such as alcohol consumption, addiction, drug consumption, senility, seizure, trauma, mental retardation, and artificial dentures [1]. In some cases, it may happen accidentally, and risk factors are not involved. In this particular case, air gun bullet has been swallowed (Figure 1). The shooter had put a bullet in his mouth in order to reload his gun and shoot rapidly; then swallowing and aspiration happened. In this case, because the foreign body is opaque, chest X-ray can be helpful for diagnosis (Figure 2). The alternative way to diagnose is fiberoptic bronchoscopy; which is sometimes considered a therapeutic strategy (Figure 3). Foreign body aspiration in tracheobronchial tree requires immediate diagnosis and removal; because the ignored objects may result in complications like infection, abscess, empyema, and haemoptysis or even bronchopleural fistula [2]. Therapeutic options to remove aspirated foreign bodies from the respiratory tract are carried out through fiberoptic and rigid bronchoscope [3]. In cases oimmediate removal of the foreign body, the outcome will be excellent; and there will be no specific complication and sequel. In some rare cases, surgery is needed to remove the foreign body; however, surgery is mostly required in situations with late diagnosis and occurrence of complications.
References
- Senturk E, Sen S. An unusual case of foreign body aspiration and review of the literature. Tuberk Toraks. 2011;59(2):173-7.
- Bahnassy AA, Diab AB. Neglected bronchial foreign body in child simulating a calcified mass lesions:Challenging computed tomography diagnosis. Int J Health Sci. 2007;1(1):107-9.
- Friedman EM. Tracheobronchial foreign bodies. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2000;33:179-85.