Research Article - Journal of Hypertension and Heart Care (2022) Volume 5, Issue 4
Level of adherence to lifestyle modifications and associated factors among hypertensive patients attending outpatient department at bishoftu general hospital, oromia region, Ethiopia, 2022.
Girma Mideksa1*, Samrawit Solomon2, Temesgen Geleta21Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia
2School of Public Health, SPHMMC, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- Corresponding Author:
- Girma Mideksa
Bishoftu General Hospital
Oromia, Ethiopia
E-mail: girmamdks@gmail.com
Received: 26-July-2022, Manuscript No. aajhhc-22-73104; Editor assigned: 28-July-2022, PreQC No. aajhhc-22-73104(PQ); Reviewed: 11-August-2022, QC No. aajhhc-22-73104; Revised: 18-August-2022, Manuscript No. aajhhc-22-73104(R); Published: 25-August-2022, DOI:10.35841/AAVRJ-6.4.116
Citation: Mideksa G, Solomon S, Geleta T. Level of adherence to lifestyle modifications and associated factors among hypertensive patients attending outpatient department at bishoftu general hospital, oromia region, Ethiopia, 2022. J Hypertens Heart Care. 2022;5(4):116
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a major public health problem affecting over one billion people worldwide. Many people live unhealthy lifestyles, which are regularly undetected and poorly controlled for hypertension. To address this issue, adherence to lifestyle modification approaches is regularly overlooked as the cornerstone of hypertension prevention and control. Objective: To assess the level of adherence to lifestyle modifications and associated factors among hypertensive patients attending outpatient departments at Bishoftu General Hospital, in 2022. Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional study design was conducted among 301 hypertensive patients between January and March 2022. A systematic random sampling technique was used. The data were collected through face-to-face interviews with participants using a structured questionnaire by trained data collectors. Data were entered into Epi-info 7.2.1.0 and exported to SPSS version 26 software for further analysis. Data were analyzed by using descriptive statistics and identified predictors of the outcome using a bivariable and multivariable logistic regression model (adjusted odds ratios with p-value <0.05 and 95% CI). Results: The study included 301 respondents with a 100% response rate.158 (52.5%) were females and the median age was 57 (±12.4 SD) years. The overall adherence in this study was only 26.9%. The study found that the patients Age older than 55 years (AOR= 2.81; 95% CI: 1.35-5.84), formal education (AOR: 0.52; 95% CI: 0.28 - 0.96), the patients who had hypertension with 5 to 10 years diagnosis time (AOR = 2.33: 95% CI: 1.01–5.37), co-morbidity (AOR=2.06; 95% CI: 1.21,3.49) and good knowledge about healthy lifestyle (AOR:0.42; 95% CI: 0.24-0,74) have an independently associated with adherence to lifestyle modifications. Conclusions: The Level of adherence to recommended lifestyle modification among hypertensive patients was low in this study. Of the variables studied, age, educational level, duration of hypertension, co-morbidities, and knowledge about healthy lifestyles were independent predictors of adherence to lifestyle modifications.
Keywords
Adherence, Lifestyle modification, Hypertension.
Introduction
Hypertension is one of the major important risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. It is the largest cause of death worldwide, accounting for 10.8 million deaths per year [1,2]. Globally, 1.39 billion people had hypertension, and one-third of adults have the condition. These 349 million people live in high-income countries, while 1.04 billion live in low- and middle-income countries, indicating a considerable increase in morbidity and death. The prevalence of hypertension is rising globally owing to the aging of the population and increases in exposure to lifestyle risk factors including unhealthy diets [3]. Among all World Health Organization (WHO) regions, the prevalence of hypertension is highest in the African region (46%) and lowest in the Americas region (35%) [4]. In terms of economic burden, poorly controlled hypertension is a fairly important public health concern among the elderly worldwide. Some studies have shown that most hypertensive patients do not have sufficient knowledge about lifestyle modification [5].
Approximately 74.7 million people in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) suffer from hypertension, which is expected to reach 125.5 million and will hinder the target set to reduce by 25% the prevalence of hypertension globally by 2025 [6,7]. In 2016, WHO and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention launched the Global Hearts Initiative to support governments in helping and treating cardiovascular disease. Ethiopia is one of the countries starting the Global Heart Initiative to address risk factors associated with noncommunicable diseases (NCD) [8].
Most behavioural risk factors, such as tobacco use and drinking, were more common in men than in women. To reduce the risk of developing hypertension, it is highly recommended lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding drinking alcohol or smoking [9].
Hypertensive patients are expected to be able to modify their lifestyles. But little is known about the magnitude of healthy lifestyles since many of the studies were conducted on hypertension in Ethiopia. That means there are only a few studies done on adherence to lifestyle modification and associated factors of hypertension to show the gap and magnitude of the problem in this study area. So, this study was to assess adherence to lifestyle modifications and their associated factors among hypertensive patients in this study area.
Methods and Materials
Study area and period
The study was conducted at Bishoftu General Hospital in Bishoftu town, Oromia region, Ethiopia. The town is found 47- kilo meters away from Addis Ababa in the eastern direction. The area of the town is 182,878 hectares with a temperature range from 11.18 to 26.5°C. The town population projection was 193,340 and out of the total, 101,108 (51%) were females. A general hospital acts as a referral hospital including some parts of the East Shoa zone rural districts. The hospital provides services for more than 1,000,000 people living in its catchment area. Data was collected from 30 January to 29 March 2022.
Study design
A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted.
Source population
All adult hypertensive patients were on follow-up at Bishoftu General Hospital.
Study population
All selected adult hypertensive patients in the outpatient department who fulfilled the inclusion criteria and be available during the study period were the study population.
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria: All hypertensive patients aged ≥18years and old who were on medical treatment for at least six months period before the beginning of the study were included in the study.
Exclusion criteria: Patients with hypertension who were unwilling to perform a 24-hour recall at home and pregnant women were excluded from the study.
Sample size Determination and Sampling Procedures
Sample size determination using adherence to lifestyle modifications
The sample size was calculated using a single population proportion formula by assuming 23.6% for the proportion of adherence to lifestyle modification with hypertensive patients from a study conducted at the Dessie Referral Hospital [10], with a 5% marginal error, and a 95% confidence level (CL). The sample size is (n) =273.
Sample size determination using risk factors associated with adherence to life style modifications among hypertension patients
The sample size required by using double population proportions to identify risk factors associated with adherence to lifestyle modifications among hypertensive patients was detected at a confidence level of 95%, variables significantly associated with hypertension in previous studies, and the power was fixed at 80% of the study. From a previous Ethiopian study, I have addressed a few factors that are strongly associated with lifestyle modifications in hypertensive patients. In a study of selected hospitals in southern Ethiopia [11], adherence to healthy lifestyle was 25.9% for patients aged over 65 years and 5.4% for patients under 65 years, with an adjusted odds ratio (AOR) of 0.27, and an analysis of similar studies recommended lifestyle modifications showed 32.2% of patients without formal education and 20.7% with formal education, with an adjusted odds ratio (AOR) of 2.00. In the Northeastern Ethiopia study, [10] adherence to recommend lifestyle modifications was 9.3% in adult hypertensive patients with comorbidities and 14.3% in those without comorbidities, with an adjusted odds ratio (AOR) of 2.37.
The sample sizes calculated accordingly were 205, 210, and 273. The sample size of the first objective was larger than the sample size of the second objective. Therefore, the final sample size was adjusted by adding a 10% non-response rate, and finite population adjustment, resulting in a total sample size of 273. Accordingly, the sample size calculated in this study was 301. Hence the sample size of 301 was the final sample size for the present study as it would suffice to address all objectives of the study.
Sampling technique and procedures
Patients found during the study period at Bishoftu General Hospital who met the inclusion criteria were included in the study and exclusively for lifestyle modification adherence. Participants in the study were selected using a systematic random sampling technique of patients with hypertension who visit the hospital at chronic follow-up departments known to be hypertensive patients based on monthly hospital reports. In 2021, a total of 3,111 hypertensive patients were divided by the sample size (n = 301) to obtain k=10.3. Finally, participants were selected for the study using a systematic sampling method, with every tenth client selected from the daily flow of interval clients based on their outpatient follow-up, and the first case being randomly selected from 1 to 10 clients.
Variables
Dependent variable
Level of adherence to lifestyle modifications
The independent variables
Socio-demographic factors: Age, sex, marital status, religion, ethnicity, level of education, occupation, residence, monthly income, and family size.
Health profile of the patients: Presence of co-morbidity (such as diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease), duration of the disease, and family history of hypertension.
Individual factors: knowledge of lifestyle modification.
Data collection instruments and procedure
Data were obtained using a structured, validated, and pretested interviewer-administered questionnaire modified from questions found in the literature and the WHO STEPS questionnaire survey [12]. There is no standard questionnaire available to assess adherence to lifestyle modifications. The questionnaire contains information about variables related to socio-demographic, personal, and knowledge of lifestyle modifications. These variables can be expressed in terms of adherence to a dietary approach to stop hypertension (DASH), regular exercise, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking.
Measurements: Dependent variables, which are adherence to lifestyle modifications, were evaluated by adapting tools from similar studies. In this study, the components of lifestyle changes were measured on the Likert scale (always, most of the time, some time, and never). For each element (regular exercise, diet, smoking cessation, drinking limitation), participants always had specific questions to answer from some time options, never. and never did so [13,14].
Data collection and data collectors
Data was collected through face-to-face interviews. Investigators are responsible for the overall management of the study. Data were selected by three Bachelor of Science (BSC) professional nurses based on their experience in outpatient clinics, and a Master of Public Health (MPH) professional was recruited for supervisory activities. The study protects patient privacy by allowing for anonymity and voluntary participation.
Data quality control
Both data collectors and supervisors were trained on the objectives, research methodology, and approach to data collection for one day. The purpose of the training was to ensure that all data collectors had the same information about the research tool and followed the same interview procedures. The training focused on the purpose of the study, confidentiality, how to approach and promote questions to clients. The questionnaire is primarily prepared in English and translated into Afaan Oromo and then translated into English by another person to verify consistency. Preliminary testing was carried out in 15(5%) of samples in health facilities that were not included in the final study. Based on the finding, grammatical sequences of questions will be arranged on questionnaires. The Principal Investigator and Supervisor checked the completeness, accuracy, and clarity of the daily data collection with the data collectors, and any necessary corrections were made before the start of the next data collection day. Finally, the data was cleaned, coded, and crosschecked using the Epi-info software before data analysis.
Data processing and analysis
The data was cleaned, coded, edited, and entered into Epi- Info version 7.2.1.0, and then exported to SPSS version 26 for further analysis. To assess the level of adherence to lifestyle modifications and associated factors among hypertensive patients, bivariable and multivariable analysis was employed. The assumptions for binary logistic regression were checked to ensure that all potential confounders were controlled and values less than 0.25 in the bi-variable analysis were considered as candidate variables for multivariable logistic regression. The model goodness of fit was assessed using the Hosmer Lemeshow test. The association between the different independent variables and with dependent was measured using a bivariable and multivariable logistic regression model (adjusted odds ratios with p-value <0.05 and 95% CI).
Operational Definitions and Measurements
Lifestyle modification
The adoption of a healthy lifestyle which was recommended by JNC 7 as non-pharmacological management of hypertension measured using physical exercise, (DASH) diet, moderation of alcohol intake, and stopping smoking [10].
Adherence to lifestyle modifications
According to JNC 7 recommended healthy lifestyles, were measured based on respondents who adhere to (DASH) diet usually or always ate a diet rich in vegetables, grains, and fruits; rarely or never ate salt, rarely or never ate saturated fat; aerobic physical activity for >30 minutes per day at least five times per week; stop smoking, and never consumed alcohol or alcohol consumed limited to 2 standard drinks a day for men and 1 standard drink a day for women. In this study, the participants who adhered to all these four healthy lifestyles were considered adherent or otherwise non-adherent [15].
Diet-related adherence
Respondents who usually or always ate a diet rich in vegetables, grains, and fruits, rarely or never ate salt; rarely or never ate saturated fat at least 3 times per week were considered to be adherent [15].
Exercise-related adherence
Respondents who engage in aerobic physical activity (including brisk walking, jogging or running, riding a bicycle and swimming) for >30 minutes per day at least five times per week. The respondents were considered adherent to the physical activity recommendation if they answered yes to the exercise inquiry and otherwise [14].
Smoking-related healthy lifestyle
Participants who self-reported to have never smoked or quit smoking within the previous 12 months [16].
Alcohol consumption-related adherence
Participants who reported that they either never consumed alcohol or alcohol consumed limited to 2 standard drinks a day for men and 1 standard drink a day for women (1 standard drink is equivalent to 25 ml spirits (e.g. whisky, brandy, vodka) or 125 ml (one standard drink glass) wine or 340 ml beer) were taken as adherent to moderation of alcohol consumption [17].
Knowledge on healthy lifestyle
Respondents with scores above the mean value on hypertension evaluation of lifestyle and management scale were taken as having good knowledge about a healthy lifestyle otherwise low [10].
Ethical considerations
Ethical clearance was obtained from the institutional review board (IRB) (Ref.No.PM23/345/2022) of St. Paul’s Hospital Millennium Medical College and Oromia Regional Health Bureau. An official letter was sent to Bishoftu general hospital. After obtaining permission from the hospital to participate in the study, an informed, voluntary, written, and signed consent was obtained for the participation of both the hospital manager and the patients. The patient's privacy and confidentiality were ensured through an interview in a non-public place, and they will be aware that their participation in the study would not be an incentive or harm. Finally, the identity of the participants remained anonymous throughout the process of data collection and analysis.
Results
Socio-demographic characteristics of participants
Out of the total hypertensive patients who attended the outpatient chronic follow-up department of Bishoftu General Hospital during the study period, 301 hypertensive patients were included in the study, giving a response rate of 100%. The majority of 212 (70.4%) study participants lived in an urban area. The median age of the participants was 57.00 years (±12.4 SD), slightly higher than half of 162 (53.8%) of the participants were found to be above the age of 55 years. The majority of participants were married 211 (70.1%), females 158 (52.5%), and 242(80.4%) of them attended formal education. Around 138 (45.8%) of the participants were Oromo by ethnicity and 212(70.4%) were Orthodox followers by religion (Table 1).
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residency | Urban | 212 | 70.4 |
| Rural | 89 | 29.6 | |
| Sex | Male | 143 | 47.5 |
| Female | 158 | 52.5 | |
| Age in years | 18-35 | 20 | 6.6 |
| 36-45 | 36 | 12.0 | |
| 46-55 | 83 | 27.6 | |
| >55 | 162 | 53.8 | |
| Marital status | Married | 211 | 70.1 |
| Single | 16 | 5.3 | |
| Divorced | 30 | 10.0 | |
| Widowed | 44 | 14.6 | |
| Ethnicity | Oromo | 138 | 45.8 |
| Amhara | 106 | 35.2 | |
| Gurage | 33 | 11.0 | |
| Tigre | 17 | 5.6 | |
| Others* | 7 | 2.3 | |
| Religion | Orthodox | 212 | 70.4 |
| Protestant | 43 | 14.3 | |
| Muslim | 38 | 12.6 | |
| Others ** | 8 | 2.7 | |
| Educational status | No formal education | 59 | 19.6 |
| Formal education | 242 | 80.4 | |
| Occupation | Employed | 88 | 29.2 |
| Unemployed | 65 | 21.6 | |
| Farmer | 65 | 21.6 | |
| Private business | 73 | 24.3 | |
| Others*** | 10 | 3.3 | |
| Average monthly income( in birr) | No regular income | 59 | 19.6 |
| 1000 ETB | 23 | 7.6 | |
| 1000-1999ETB | 49 | 16.3 | |
| 2000-2999ETB | 111 | 36.9 | |
| >3000ETB | 59 | 19.6 | |
| Family Size( in number) | <5 | 163 | 54.2 |
| >5 | 138 | 45.8 |
Table 1. Socio-demographic characteristics of hypertensive patients attending the outpatient department at Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia, 2022 (n = 301).
Health profile of the Patients and Individual related factors
Out of 301 study participants, 122 (40.5%) have a family history of hypertension and 130(43.2%) were hypertensive for five or more years. Among the study participants, 129 (42.9%) participants had co-morbidities diseases (such as diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease) (Table 2).
| Variable | Category | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family history of hypertension | No | 179 | 59.5 |
| Yes | 122 | 40.5 | |
| Duration of hypertension (years) | <2 | 44 | 14.6 |
| 2-5 | 78 | 25.9 | |
| 5-10 | 130 | 43.2 | |
| >10 | 49 | 16.3 | |
| Presence of comorbidity | No | 172 | 57.1 |
| Yes | 129 | 42.9 |
Table 2. Patient health profile and individual factors of study participants at Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia, 2022(n = 301).
Knowledge on a healthy lifestyle
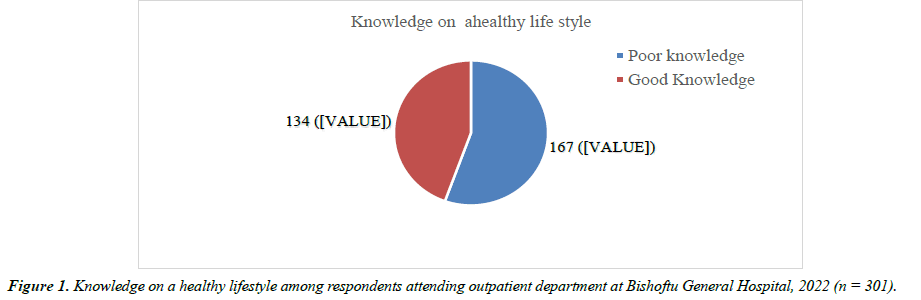
The knowledge and information on a healthy lifestyle addressing hypertension patients was determined using ten (10) questions for hypertension evaluation on a healthy lifestyle. The average knowledge score was (2.01 ± 0.415) as the cut-off point, indicating that 134 (44.5%) of the 301 participants were good knowledge on a healthy lifestyle (Figure 1).
Level of Adherence to Recommended Lifestyle Modifications
Adherence to the recommended diet
The majority 174 (57.8%) of participants included fruits, vegetables, and grains in their diet after being diagnosed with hypertension. The average dietary score was found to be (3.246 ± 0.594). Among 167(55.5%) respondents sometimes ate foods rich in saturated fats, and 85(28.2%) participants rarely ate spicy foods after diagnosis. About 112(37.2%) of participants never eat salt in food during their meals (Table 3).
| Variables | Always | Often | Sometimes | Rarely | Never |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Included fruits, vegetables, and grains in the diet | 71(23.6%) | 33(11%) | 132(43.9%) | 39(13%) | 26(8.6%) |
| Consuming foods that contain high saturated fat | 24(8%) | 15(5%) | 167(55.5%) | 59(19.6%) | 36(12%) |
| Consuming spicy foods | 31(10.3%) | 40(13.3%) | 109(36.2%) | 85(28.2%) | 36(12%) |
| Consuming salt in your food | 7(2.3%) | 15(5%) | 104(34.6%) | 63(20.9%) | 112(37.2%) |
Table 3. Adherence to the recommended diet among hypertensive patients attending Bishoftu General Hospital outpatient department, Oromia, Ethiopia, 2022 (n = 301).
Adherence to related-Exercise
About 152(50.5%) of participants said they do physical activity, with 69(22.6%) claiming they exercise at least 3 times a week, and about a similar number 66(21.9%) confirming that they engage in an activity that takes greater than 30 minutes of practice. Aerobic exercise (including brisk walking, jogging or running, riding a bicycle and swimming) was the most common physical activity among those found to be consistent at 126(41.9%) (Table 4).
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do you perform physical exercise? | No | 149 | 49.5 |
| Yes | 152 | 50.5 | |
| Frequency of exercise in a week | <Three times per week | 44 | 14.6 |
| Three times per week | 69 | 22.9 | |
| >Three times per week | 44 | 14.6 | |
| Duration of exercise per session | Less than 30 minutes | 35 | 11.6 |
| From 30 minutes to 1 hour | 66 | 21.9 | |
| More than 1 hour | 58 | 19.3 | |
| Type of exercise performed | Aerobics(walking, Jogging) | 126 | 41.9 |
| Weight-bearing | 15 | 5.0 | |
| Driving | 13 | 4.3 | |
| Dancing | 5 | 1.7 |
Table 4. Adherence to related-Exercise among hypertensive patients attending Bishoftu General Hospital outpatient department, Oromia, Ethiopia, 2022 (n = 301).
Alcohol consumption
All 273 (90.7%) hypertensive patients were adhere to moderation in alcohol consumption. About 105(34.9%) of the participants consumed less than one drink per week and 25(8.3%) of the participants consumed more than seven drinks per week. Approximately 128 (46.9) of these participants confirmed that a relative/health care professional was concerned about their alcohol use and advised them to reduce their alcohol consumption during the last year (Table 5).
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol consumption | Not moderated | 28 | 9.3 |
| Moderated | 273 | 90.7 | |
| How often do you usually drink alcohol | <1 drink a week | 105 | 34.9 |
| 1-3 drinks a week | 96 | 31.9 | |
| 4-6 drinks a week | 47 | 15.6 | |
| = 7 drinks a week | 25 | 8.3 | |
| Never | 28 | 9.3 | |
| Tried to quit Alcohol consumption | No | 145 | 53.0 |
| Yes | 128 | 46.9 |
Table 5. Participant response to alcohol consumption among hypertensive patients attending outpatient follow-up at Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, 2022 (n = 301).
Smoking cessation
Many of the current problems from coastal development have arisen due to a lack of planning or at least a lack Of the 301 participants, 274 (91.0%) had never smoked, while 27 (9.0%) of them are still smokers. Among the 27 participants who still smoked cigarettes, 18 (66.7%) had tried to quit smoking (Table 6).
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ever smoked cigarette | No | 274 | 91.0 |
| Yes | 27 | 9.0 | |
| Advice by a health worker to quitting smoking | No | 3 | 11.1 |
| Yes | 24 | 88.9 | |
| Tried to quit smoking | No | 9 | 33.3 |
| Yes | 18 | 66.7 |
Table 6. Participant response on Smoking cessation among hypertensive patients attending the outpatient department at Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, 2022 (n=301).
Overall the level of adherence to recommended lifestyle
The overall the level of adherence to recommended lifestyle (including diet, exercise, moderation of alcohol consumption, and smoking cessation) in this study found that only 26.9% of participants adhere to all recommended lifestyle modifications. About 174(57.8%) of participants adhere to recommendations related to the diet. Most 177(58.8%) participants did not engage in regular exercise at least 3 days per week, with a minimum duration of 30 minutes. About 274 (91.0%) participants did not smoke, and 273(90.7%) participants remained with moderate alcohol consumption (Table 7).
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diet-related adherence | Non-adherent | 127 | 42.2 |
| Adherent | 174 | 57.8 | |
| Exercise-related adherence | Non-adherent | 177 | 58.8 |
| Adherent | 124 | 41.2 | |
| Alcohol consumption | Not moderated | 28 | 9.3 |
| Moderated | 273 | 90.7 | |
| Smoking | Ceased | 274 | 91.0 |
| Did not ceased | 27 | 9.0 | |
| Overall adherence to recommended lifestyle | Non-adherent | 220 | 73.1 |
| Adherent | 81 | 26.9 |
Table 7. Overall the level of adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications for hypertensive patients attending outpatients at Bishoftu General Hospital, Ethiopia in 2022 (n = 301).
Factors associated with adherence to lifestyle modifications
In Bivariable logistic regression analysis study showed that age, marital status, educational status, occupational status, family membership, duration of hypertension, having co-morbidities, and knowledge about lifestyles were significantly associated with adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications at a p-value ≤ 0.25. The Hosmer and Leme show the goodness of fit test gave a p-value = 0.212 suggestive of evidence of fitness of the model. After controlling for the influence of other factors (confounders) in a multivariable logistic regression, age, educational status, duration of hypertension, having comorbidities, and knowledge about lifestyles were found to be significantly associated with adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications at a p-value ≤ 0.05.
Respondents in the elderly group were found to be nearly three times more adherent than respondents in the young age group (AOR 2.81; 95% CI: 1.35, 5.84). Formal education respondents were 48% less likely to be adherent to lifestyle modification (AOR = 0.52; 95% CI: 0.28, 0.96) compared to respondents with no formal education. Patients who had hypertension for long-duration were almost twice as likely to adhere to patients as short as diagnosis (AOR = 2.33: 95% CI: 1.01–5.37). Adult hypertensive patients with co-morbidities were about two (AOR=2.06: 95% CI: 1.21-3.49) times more likely to adhere to recommended lifestyle modifications than patients without co-morbidities. Patients with good knowledge about lifestyles were 58% less likely to adhere to recommended lifestyle modifications than those with less knowledge about lifestyles (AOR = 0.42: 95% CI: 0.24-0.74) (Table 8).
| Variables | Category | Lifestyle adherence | COR (95%CI) | AOR (95%CI) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adherent N (81) | Non-adherent N (220) | |||||
| Age in years | 18-35 | 7 | 13 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 36-45 | 10 | 26 | 1.28(0.39-4.22) | 0.92(0.29-2.85) | 0.891 | |
| 46-55 | 11 | 72 | 0.97(0.39-2.42) | 1.07(0.45-2.51) | 0.869 | |
| >55 | 53 | 109 | 0.90(0.16-0.77)* | 2.81(1.35-5.84) ** | 0.006 | |
| Marital status | single | 6 | 10 | 0.45(0.13-1.58)* | 0.56(0.14-2.20) | 0.408 |
| Married | 47 | 164 | 0.47(0.10-2.30) | 1.70(0.37-7.79) | 0.491 | |
| Divorced | 6 | 24 | 1.47(0.35-6.15) | 1.81(0.53-6.12) | 0.340 | |
| Widowed | 22 | 22 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Educational status | No- formal education | 22 | 37 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Formal-education | 59 | 183 | 0.48(0.24-0.97)** | 0.52(0.28-0.96)** | 0.037 | |
| Occupational status | Employed | 19 | 69 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Unemployed | 19 | 46 | 3.53(0.38-32.41) | 0.35(0.04-3.06) | 0.349 | |
| Farmer | 25 | 40 | 3.61(0.39-33.44) | 0.26(0.03-2.23) | 0.220 | |
| Private business | 17 | 56 | 10.65(0.94-120.62)* | 0.17(0.021-1.48) | 0.109 | |
| Other | 1 | 9 | 3.18(0.34-29.17) | 0.32(0.03-2.77) | 0.304 | |
| Family size (numbers) | <5 | 47 | 116 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| >5 | 34 | 104 | 0.80(0.37-1.19)* | 0.76(0.45-1.28) | 0.304 | |
| Duration of hypertension ( years) |
<5 | 21 | 75 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 5-10 | 29 | 89 | 0.85(0.35-2.09)* | 2.33(1.01-5.37)** | 0.047 | |
| 10-15 | 15 | 36 | 0.20(.07-.53) | 1.96(0.88-4.36) | 0.099 | |
| >15 | 16 | 20 | 0.79(.36-1.69) | 1.61(0.64-4.00) | 0.304 | |
| Co-morbidities | No | 35 | 137 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 46 | 83 | 2.01(1.19-3.73)* | 2.06(1.21-3.49)** | 0.007 | |
| Knowledge level | Poor | 58 | 109 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Good | 23 | 111 | 0.38(0.24-.80) * | 0.42(0.24-0.74) ** | 0.003 | |
Table 8. Bivariable and Multivariable Logistic regression output indicating factors associated with Adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications among patients with hypertension attending the outpatient department at Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia,2022 (n=301).
Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the level of adherence to lifestyle modifications and associated factors among patients with hypertension attending the outpatient department at Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia. In this study, the level of good adherence to the recommended lifestyle modification among patients with hypertension was found to be 26.9%. Age, educational status, duration of hypertension, having co-morbidities, and knowledge about lifestyle were significantly associated with adherence to lifestyle modification. So, hypertension is the most important public health problem, if poorly managed and poor adherence to a healthy lifestyle this factor that can lead to disability and mortality. As a result, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an effective strategy for reducing hypertension.
Overall the level of adherence to recommended lifestyle modification in this study was only 26.9%. This is low compared to studies conducted in Ghana and eastern Ethiopia that reported adherence rates of (72%) and (28.7), respectively [18,19]. The discrepancy in adherence rates between our study and other studies may be due to the various study methods (like sample size) and inadequate health promotion given to the client regarding knowledge on a healthy lifestyle of hypertension prevention and control. This study found that although many people still don't adhere to a healthy lifestyle, this increases the burden of chronic diseases like hypertension.
In this study dietary adherence was described by including more fruits, vegetables, and grains in the diet, as well as eating low-sodium and low fat. The prevalence of dietary adherence in this study was 57.8%. In contrast, in Korea, this study shows that a majority (77.5%) of the study participants followed dietary modification and another study from Addis Ababa found that only (64.7%) of the respondents were found to be adherent [20,21]. Discrepancies in local studies may be due to differences in dietary habits and the place of residence of study participants. Hypertension was successfully reduced in those who followed a recommended diet.
In this finding, exercise-related adherence was 41.2%. Similar studies conducted in Bangladesh and Georgia found slightly higher adherence rates of (46%) and (46.6%), respectively [22,23]. This finding is comparable with the adherence level of participants to exercises at a public health hospital in Addis Ababa, in which (33.9%) adhere to exercise regularly [24]. Discrepancies in the study area could be the result of hardworking circumstances, a lack of awareness of promotions for those with low educational attainment, cultural differences, and a lack of organized living conditions. This indicates that a lack of exercise adherence is a leading cause of hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
The majority in this study 90.7% of respondents were found to moderate their alcohol consumption. In similar studies conducted in Malaysia and Korea and almost (90%) and (80%) of the study, participants were limited to alcohol consumption [14,25]. Another study conducted in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, when compare the results shows that (74.8%) of respondents moderated their alcohol consumption [26]. This disparity can be explained by social and cultural norms that support the consumption of alcoholic beverages. This means that consuming alcohol raises the risk of hypertension.
The majority in this study 91% had never smoked before twelve months, which is consistent with studies in Zimbabwe (97%) and Turkey (83%) where the majority of respondents were found to be adherent to smoking cessation [17,27]. In a similar study in selected hospitals, in southern Ethiopia, 91.2% were non-smokers (11). One of the leading causes of hypertension is smoking. This similarity can be explained by social and cultural practices in society that discourage smoking.
In this study, age, education level, duration of hypertension, having co-morbidities, and knowledge about lifestyles were strongly associated with adherence to the recommended lifestyle modifications.
It was found that older respondents are more adherent to lifestyle modifications than younger age groups. In a similar study conducted in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, it was found that individuals above the age of 60 years were more likely to recommend lifestyle modifications [26,28]. The reason for the older age differences may be further explained by increased awareness of the management and control of hypertension during visits to health care providers.
Those with formal education were 48% less likely to adhere to lifestyle modification than respondents with no formal education. This study is supported by Eritrea and Gondar, Ethiopia [29,30]. A possible explanation may be related to an increase in patients' awareness of the importance of recommended lifestyle modification to prevent hypertension with increasing formal education levels.
In this study respondents who reported that they have been diagnosed longer period since diagnosis with hypertension for a short period were found more likely to be adherent. This is comparable to a study from southern Ethiopia and Ghana, which found that Patients on treatment with a long history of hypertension were more likely to adhere to lifestyle modifications [11,18]. The results showed that those who have had hypertension for less than five years are less likely to see the condition as life-threatening, while those with hypertension for more than five years are more likely to adhere to lifestyle modification. The differences are due to the continuous counseling and health education provided by healthcare providers.
This study showed that adult hypertensive patients with comorbidities were twice as likely to adhere to the recommended lifestyle modifications compared to those without comorbidities. It is very difficult to control hypertension if it is accompanied by other co-morbidities. This could make it harder for the patient to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, making their conditions worse. The study was conducted in Saudi Arabia and north-eastern Ethiopia [10,28]. A possible rationale could be that patients with comorbidities visit health care providers more frequently and pay more attention to their health status, as evidenced by better commitment to lifestyle changes.
This study indicated that knowledgeable patients were 58% less likely to adhere to lifestyle modifications than less knowledgeable patients. Hypertension knowledge is an important part of the chronic care model, and knowing how to prevent and control the disease is an important part of managing it. This finding was consistent with findings of studies conducted in hospitals in Gondar, Ethiopia, and Eastern Ethiopia [30,31]. This may be because poor knowledgeable patients may not understand the disease and how to prevent and manage it. It is important to increase patient access to information on risk factors and lifestyle modification recommendations.
The main limitation of this study it was conducted only at a single public health hospital and did not include patients with hypertension who were seen in private clinics. In addition, research methodologies involving self-reported measures depend largely on individuals. This method is simple but less reliable among those patients who deny poor adherence and social desirability bias, especially among smokers, and recall bias may exist.
Conclusion
This study revealed the level of adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications was low among patients with hypertension. Of the variables studied, age, educational level, duration of hypertension, having co-morbidities, and knowledge about healthy lifestyle were independent predictors of adherence to lifestyle modifications.
Abbreviations and Acronyms
AOR: Adjusted Odd Ratio, BP: Blood Pressure, CVD: Cardiovascular Diseases, DASH: Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, EDHS: Ethiopian Demography and Health survey, HTN: Hypertension, HC: Health Center, JNC7: Seventh Report of Joint National Committee, Mm Hg: Millimeters of Mercury, NCD: Non-Communicable Disease, SPHMMC: St. Paul’s Hospital Millennium Medical College, WHO: World Health Organization.
Author’s Contribution
GM, SS and TG made a substantial contribution to the conception design, acquisition and interpretation of data. GM drafted the manuscript and carried out rigorous editorial work. All authors revised the paper critically for the intellectual contents. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author’s Information
GM1, 2 Bishoftu General Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia. SS1, TG1 School of Public Health, St. Paul’s Hospital Millennium Medical College, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Funding
St. Paul’s Hospital Millennium Medical College fully covered the financial issues to handle this research.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Acknowledgments
I would like to acknowledge St. Paul’s hospital millennium medical college, School of public health for giving me an opportunity of learning Master of public health in Field Epidemiology and the broad knowledge shared with us during class sessions. I would like to thank my Advisors Dr. Samrawit Solomon (MD, MPH, Associate Professor) and Mr. Temesgen Geleta (MPH) for their constructive advice, guidance, and comments, at each step of the research development. We also thank the Bishoftu General Hospital managers, study participants, and all those who have been very contributed and cooperative during data collection.
References
- Forouzanfar MH, Liu P, Roth GA, et al. Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115mmHg, 1990-2015. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc. 2017;317(2):165–82.
- Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi-Kangevari M, et al. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1223–49.
- Mills KT, Stefanescu A, He J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(4):223–37.
- Dhar L, Dantas J, Ali M. A Systematic Review of Factors Influencing Medication Adherence to Hypertension Treatment in Developing Countries. Open J Epidemiol. 2017;07(03):211–50.
- Al-wehedy A, Hassan S, Elhameed A, et al. Effect of Lifestyle Intervention Program on Controlling Hypertension among Older Adults. Journal of Education and Practice. 2014;15(5), 61-71.
- Omar SM, Musa IR, Osman OE, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of hypertension among adults in Gadarif in eastern Sudan: A community-based study. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):4–9.
- Cohen DL, Townsend RR, Angell SY, et al. The World Health Organization recognizes noncommunicable diseases and raised blood pressure as global health priority for 2025. J Clin Hypertens. 2014;16(9):624–624.
- OMS. Technical package for cardiovascular disease management in primary health care. Report. 2016.
- Ethiopian Public Health Institute. (2016). Ethiopia STEPS report on risk factors for non‐communicable diseases and prevalence of selected NCDs.
- Andualem A, Gelaye H, Damtie Y. Adherence to lifestyle modifications and associated factors among adult hypertensive patients attending chronic follow-up units of dessie referral hospital, north east Ethiopia, 2020. Integr Blood Press Control. 2020;13:145–156.
- Buda ES, Hanfore LK, Fite RO, et al. Lifestyle modification practice and associated factors among diagnosed hypertensive patients in selected hospitals .Clinical hypertension. 2017; 23(1):1–9.
- WHO 2016. WHO STEPwise Risk-Factor Chronic Disease Approach to Surveillance. 2016;
- Angelo AT, Geltore TE. Lifestyle modification practice and associated factors among diagnosed hypertensive patients in Mizan Tepi University Teaching Hospital South west Ethiopia, 2019: cross-sectional study. PAMJ Clin Med. 2020;2(156):1–12.
- Habib N, Kailash K, Rashid M. Lifestyle modification practice in rural community at Kedah in Malaysia: A cross sectional study. SBV Journal of Basic Clinical and Applied Health Science. 2018; 1(1):19-26.
- Verdecchia P, Angeli F. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on the Prevention , Detection , Evaluation , and Treatment of High Blood Pressure : The Weapons Are Ready. Revista espanola de cardiologia. 2003; 56(9): 843-47.
- Nadewu AN, Geda B. Adherence to Healthy Lifestyle among Hypertensive Patients in Harar Region, Eastern Ethiopia. Prim Heal Care Open Access. 2018;8(4):1-7
- Tozivepi SN, Takawira S, Chikaka E, et al. The nexus between adherence to recommended lifestyle behaviors and blood pressure control in hypertensive patients at mutare provincial hospital, zimbabwe: A cross-sectional study. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2021;15:1027–37.
- Obirikorang Y, Obirikorang C, Acheampong E, et al. Adherence to Lifestyle Modification among Hypertensive Clients : A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. Open Access Library Journal. 2018;5(2):1–13.
- Nadewu AN. Adherence to Healthy Lifestyle among Hypertensive Patients in Harar Region. Primary Health Care : Open Access. 2018;8(4):1-7.
- Shim J, Heo JE, Kim HC. Factors associated with dietary adherence to the guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension among Korean adults with and without hypertension. Clinical hypertension. 2020; 26(1):1–11.
- Patients H, Black A, Hospital L, et al. Assessments of adherence to hypertension managements and its influencing factors among hypertensive patients attending black lion hospital chronic follow up unit, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia-a cross-sectional study. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 2013;4(3):1086–95.
- Islam FMA, Hosen MA, Islam MA, et al. Knowledge of and Intention to Participate in Physical Activity Programs and Their Associated Sociodemographic Factors in People with High Blood Pressure in a Rural Area of Bangladesh : Initial Investigation from a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(18):9561.
- Fang J, Moore L, Loustalot F, Yang Q, Ayala C, Activity P. HHS Public Access. 2016;10(3):252–62.
- Aynalem GA, Alemu T, Tadesse T, et al. Factors affecting adherence to lifestyle modification among patients with hypertension at Yekatit 12 Hospital Medical College , Addis Ababa , Ethiopia , 2019. SAGE open medicine. 2021;9: 20503121211012523.
- Kim Y, Kong KA. Do hypertensive individuals who are aware of their disease follow Lifestyle recommendations better than those who are not aware? PLoS One. 2015;10(8):1–13.
- Tibebu A, Mengistu D. Adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications and factors associated for hypertensive patients attending chronic follow-up units of selected public hospitals in Addis Ababa , Ethiopia. Patient preference and adherence.2017;323–30.
- Arslan F. The assessment of adherence of hypertensive individuals to treatment and lifestyle change recommendations. Treatment of Hipertansiyonlu individuksin ve yazham bichim velarinine. 2014.
- Elbur AI. Level of adherence to lifestyle changes and medications among male hypertensive patients in two hospitals in taif; kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;7(4):168–72.
- Idris BIM, Wolday SJ, Abraham B, et al. Factors Influencing Lifestyle Modification Practice among Hypertensive Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study in two Selected Eritrean Hospitals. J Clin Images Med Case Rep. 2020;20(4):1225.
- Smachew M, Melak MF, Atenafu A, et al. Lifestyle Modification Practice and Associated Factors Among Diagnosed Hypertensive Patients in Selected Hospitals in Central Gondar Zone. Nutrition and Metabolic Insights.2022; 15:11786388221088245.
- Bogale S, Mishore KM, Tola A, et al. Knowledge, attitude and practice of lifestyle modification recommended for hypertension management and the associated factors among adult hypertensive patients in Harar, SAGE Open Medicine. 2020;8:2050312120953291.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref