Case Report - Otolaryngology Online Journal (2016) Volume 6, Issue 3
Otolaryngologic Manifestations of Sanjad Sakati Syndrome- A Case Report
- *Corresponding Author:
- Segana Hasan Abdul Cader
Department of ENT, Sur Hospital, South Sharqiya region, Sur, Sultanate of Oman
E-mail: dr_shac@yahoo.com
Received date: March 18, 2016; Accepted date: June 10, 2016; Published date: June 13, 2016
Abstract
Sanjad-Sakati syndrome (SSS) or hypoparathyroidismretardation- dysmorphism (HRD) or Middle East syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic manifestation seen predominently from the Middle East and Arabian Peninsula. Children affected with this condition are typically born with features of intrauterine growth retardation and present early with hypocalcaemic convulsions, typical facial dysmorphic features, severe growth retardation, developmental delay, low IQ and congenital hypoparathyroidism1,2. The condition is caused by mutations or deletions in the TBCE gene on Chromosome No.1 the locus is 230 kb region of gene with mutations in individuals who are affected3.There are exceptional cases who are not affected due to a TCBE gene abnormality4
Abstract
Sanjad-Sakati syndrome (SSS) or hypoparathyroidismretardation- dysmorphism (HRD) or Middle East syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic manifestation seen predominently from the Middle East and Arabian Peninsula. Children affected with this condition are typically born with features of intrauterine growth retardation and present early with hypocalcaemic convulsions, typical facial dysmorphic features, severe growth retardation, developmental delay, low IQ and congenital hypoparathyroidism [1,2]. The condition is caused by mutations or deletions in the TBCE gene on Chromosome No.1 the locus is 230 kb region of gene with mutations in individuals who are affected [3].There are exceptional cases who are not affected due to a TCBE gene abnormality [4].
Keywords
Hypoparathyroidism, Facial dysmorphism, Recurrent ear infections
Introduction
To date, fewer than 20 reports have been published worldwide in English discussing SSS. Overall, consanguinity was found in 2 of our 3 patients.
Patients with SSS typically present in the newborn period with tetany, seizures, or apnea due to hypocalcemia and recurrent infections, probably due to immune defects [5]. In the present study, most of the cases had been diagnosed during the neonatal period due to hypocalcemia/seizures or apnea, phenotypic pictures, or raised awareness of the syndrome among affected families. The syndrome has a wide variety of clinical features, including deep-set eyes, micrognathia, thin lips, small maxilla, severely decayed teeth, beaked noses, depressed nasal bridges, external ear anomalies, small hands and feet, short stature, and learning difficulties [6]. In addition, hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcemia are constant findings. All of our patients showed the cardinal features described previously
Neurological manifestations in the form of microcephaly, developmental delay, mental retardation, and seizures were reported in all patients. Speech was not affected grossly but they have some problems of articulation and they do well after speech therapy and they develop intelligible speech thereafter, some showed abnormal EEG tracings
Case report
Here we present three children with following details who presented to us in ENT department of Sur Hospital, Oman multiple times as Outpatient with recurrent ear infections and upper respiratory infections. The following chart details the various features as below. This has been prepared based on computer retrospective records of case progress of these patients (Tables 1,2).
| Features | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 6 years | 7 years | 2 years |
| Date of Birth | 2009 | 2008 | 2013 |
| Sex | Female | Female | Male |
| Birth weight | 1325 gms | 1450 gms | 1950 gms |
| Onset of symptoms | 20 days after birth | 18 days after birth | 22 days after birth |
| Mental and motor development | Delayed milestones | Delayed milestones | Delayed milestones |
| Consanguinity | First degree | First degree | No |
| Micrognathia | Present | Present | No |
| Retrognathia | Present | No | No |
| Prominent forehead | Present | Present | No |
| Deep set eyes | Present | Present | Mild |
| Thin lips | Present | Present | Present |
| Depressed nasal bridge | Present | Present | Present |
| Beaked nasal tip | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Low set ears(fig 1) | Present | Present | Normal ears |
| Big rotated ears | Yes | No | No |
| Microtia | No | No | Minimal |
| Lips | Thin lips with long philtrum | Thin lips | Thin lips |
| Tooth decay(fig 2) | Dental decay | Dental decay | Minimal decay |
| Palatal arch | Narrow | Normal | Normal |
| Ear infections | Recurrent pseudomonas otitis | Recurrent pseudomonas otitis | Recurrent AOM |
| Otoacoustic emission | Bilateral passed | Bilateral passed | Bilateral passed |
| Speech | Articulaton defect | Mild articulation problem | Delayed speech |
| Stertor | Mild | No | No |
| Latest weight | 5500 GMS | 6400 GMS | 7200 GMS |
| Radiological findings | Nephrocalcinosis | Nephrocalcinosis | Normal |
| Calcium level N-2.3 to2.8 mmol/l |
2.28 | 2.3 | 1.66 |
| Phosphate level(n-1.45 to 2.16 mmol/l) | 2.8 | 1.50 | 2.71 |
| Pth (n-10-60 micromol/l) | <0.3 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Creatinine | 19.99 uMol/l | 31.8 uMol/l | 21.3uMol/l |
| Immunoglobulin levels | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Chromosomal analysis | C.155-166 del 12 bp Homozygous | 46 XX Normal Karyotype | 46 XY Normal Karyotype |
| Others associations | Nephrocalcinosis, Hypothyroidism, Epilepsy,pinoscrotal hypoplasia and short penis | Labial fusion, vaginal atresia, Epilepsy | Epilepsy |
| Outcome of patient | Expired | Alive | Alive |
Table 1: Computer retrospective records of case progress of these patients.
| Country | Number of reported cases | Clinical features | Genetic defect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kuwait | 21 | Short stature, microcephaly, deep-set eyes, blue sclera, large floppyear lobule, small hands and feet, mental retardation,hypoparathyroidism, and hypocalcemia | c.155-166del |
| Qatar | 8 | Dysmorphology, deep-set eyes, depressed nasal bridge with beakednose, long philtrum, thin upper lip, micrognathia, large floppy earlobes, abnormal skeletal survey, developmental delay,hypoparathyroidism, hypocalcemia, and hyperphosphatemia | Not available |
| Belgium | 2 | Facial dysmorphism, short limbs, small hands and feet, smallgenitalia, hypoparathyroidism, and severe pre- and postnatal growthretardation | C.H.: c.66-67del c.1113T>A |
| Jordan | 8 | Short stature, microcephaly, deep-set eyes, small hands and feet,mental retardation and learning difficulties, hypoparathyroidism,hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and low levels of PT | c.155-166del |
| This report | 3 | Dysmorphism, preominent forehead, triangular face with deep-set eyes, abnormalexternal ear, wide depressed nasal bridge, bulbous nasal tip,antevertednares, long philtrum, thin lips and downturned corners ofmouth. The hands and feet were short, hypocalcemia,hyperphosphatemia, low levels of phosphorus | c.155-166del |
Table 2: Comparitive review of genetic and clinical data of Sanjad Sakati Syndrome
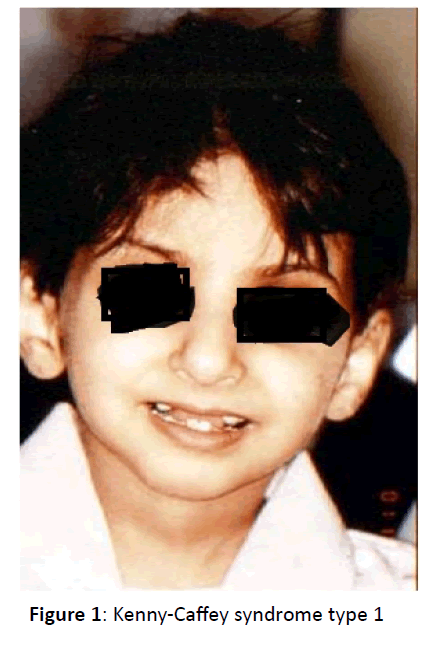
This syndrome has to be differentiated from Kenny-Caffey Syndrome which often shows cortical thickening of long bones with medullary stenosis, macrocephaly or normocephaly, normal mentality and immune deficiency. Kenny-Caffey Syndrome type 1 may show the same mutation in the tubulin specific chaperone-E gene [7] (Figure 1).
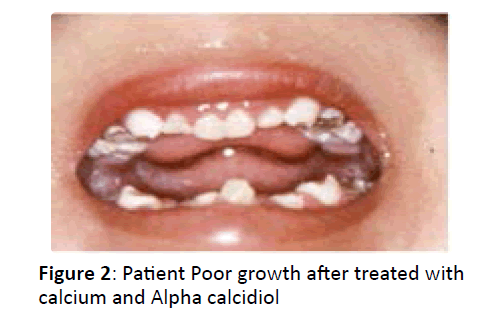
Patients’ hypocalcaemia is usually treated with calcium and alpha calcidiol as we treated our patients. However they tend to continue having poor growth. Attempts to use growth hormone in some of the cases proved unsuccessful [8]. Most patients tend to die early with recurrent infections, but rare cases have survived up to the age of 18 years [9] (Figure 2).
Conclusion
SSS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that is not uncommon in the Gulf and Arabian Peninsula. Most of the ENT manifestations are grossly present and children report due to various manifestation of poor immunity with chronically discharging ear, frequent rhinorrhea and upper respiratory infections. This case report details various facial and other clinical presentations involving SSS. Prevention of this syndrome may be achieved in the future through pre-implantation genetic diagnosis and carrier detection.
References
- Sanjad S, Sakati N, Abu-Osba YK, kaddora R, Milner RDG (1991) A new syndrome of congenital hypopatathyroidism,seizure, growth failure and dysmorphic features. Arch Dis Childhood London 66: 193-196
- Kalam MA, Hafeez W (1992) Congenital hypoparathyroidism, seizure, extreme growth failiure with developmental delay and dysmorphic features-another case of this syndrome. Clin Genet 42: 110-113.
- Parvari R, Hershkovitz E, Grossman N, Gorodischer R, Loeys B, et al. (2002) Mutation of TBCE causes hypoparathyroidism-retardation-dysmorphism and autosomal recessive Kenny-Caffey syndrome. Nature Genet 32: 448-452
- Courtens W, Wuyts W, Poot M, Szuhai K, Wauters J, et al. (2006) Hypoparathyroidism-retardation-dysmorphism syndrome in a girl: a new variant not caused by a TBCE mutation--clinical report and review. Am. J. Med. Genet. 140A: 611-617
- Naguib KK, Gouda SA, Elshafey A (2009) Sanjad-Sakati syndrome/Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 1: a study of 21 cases in Kuwait. East Mediterr Health J 15: 345–352
- Parvari R, Hershkovitz E, Kanis A (1998) Homozygosity and linkage-disequilibrium mapping of the syndrome of congenital hypoparathyroidism, growth and mental retardation, and dysmorphism to a 1-cM interval on chromosome 1q42-43. Am J Human Genet 63: 163-169.
- Naguib KK, Gouda SA, Elshafey A, mohammed F, Bastaki L, et al. (2009) Sanjad –Sakati syndrome/kenny-Caffey syndrome type 1: a study of 21 cases in Kuwait.Eastern Mediterranean health Journal 15: 345-352
- Rafique B, Al-Yaarubi S (2010) Sanjad-Sakati Syndrome in Omani children. OMJ 25: 227-229.
- Tanna N, Preciado DA, Brian N (2009) The otolaryngologic features of SanjadSakatisyndrome.Archotolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135: 7.