Research Article - Journal of Physical Therapy and Sports Medicine (2021) Volume 5, Issue 4
Acute effects of two difference volume of resistance exercises on cardiac hormones, angiotensin- II and lipolysis markers in active young male
Nikseresht Ali1*, Nikseresht Amjad2, Ahmadizad Sajad21Faculty of sport sciences, Razi University of Kermanshah, Iran
2Faculty of Sport Sciences and health. Shahid-Beheshti University of Tehran, Iran
- *Corresponding Author:
- Nikseresht Ali
Faculty of sport sciences
Razi University of Kermanshah, Iran
E-mail: nik.razi.ac@gmail
Accepted on July 28, 2021
Citation: Ali N, Amjad N, Sajad A. Acute Effects of Two Difference Volume of Resistance Exercises on Cardiac Hormones, Angiotensin- Ii And Lipolysis Markers in Active Young Male.2021:5 (4):1-7.
Abstract
Objective: The natriuretic peptides (NPs) are endogenous cardiac hormones that have been entered in current guidelines for the diagnosis of heart problems. Resistance exercise (RE) has a beneficial effect on the NPs secretion, but there is limited research on what type of volume training of RE is appropriate. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to compare the pro-ANP, NT-pro-BNP, ANG-II, NEFA and Glycerol response during the RE with different volumes. Methods: Fifteen active men volunteers (age, 26.1 ± 0.9; years; weight, 74.4±1.9 kg; height, 176.3±1.3 cm) after determination of their strength (10-Repetition Maximum) performed two resistance exercise trials with a one-week interval. subjects performed similar resistance protocols while only set frequencies were differing (three-set or five-set for ten movements). Blood samples were taken in three times including, reference point, 3 and 30 minutes after exercise. Data were analysed using two-way repeated measures of ANOVA. Results: Finding revealed that resistance exercise high-volume has a significant effect on increase NT-pro-BNP (p=0.041) but the increment in ANP and decrement ANG-II was not meaningful. Additionally, lipolysis concentrations as a result of resistance exercise (increased in glycerol and decreased in NEFA) were significant without meaningful between protocols. Conclusion: Significant augment in NT-pro-BNP due to resistance high-volume (five-set) and synchronized overdrive neuro hormonal with left-ventricular dysfunction demonstrate that resistance exercise high-volume might be related to changes in pressure inside the heart that can contribute to heart problems.
Keywords
Resistance exercise volume, Pro-ANP, NT-pro-BNP, NEFA, Glycerol.
Introduction
The natriuretic peptides (NPs) containing atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) which are secreted from cardiomyocytes in response to atrial and ventricular wall stretch, respectively [1]. It is also, a wellknown cardiovascular biomarker for early-stage determination in patients with cardiac failure, aortic stenosis, and LVventricular dysfunctions [2-4]. Indisputably, NPs secretion involves two fundamental physiological systems, including cardiovascular homeostasis and energy expenditure. Their roles have resulted in reducing blood pressure, cardiac burden, decline renin-angiotensin system and increase renal sodium and water excretion. Lipolysis enhancement is another worthwhile action of NPs, they are associated with increased oxidation of fatty acid in both human fatty tissue and skeletal muscles. Furthermore, specified features of cardiac muscle in uptake free fatty acid are lead to these cardiac hormones contributing to increased plasma levels of non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) [5]. On the contrary, the renin-angiotensin system is known as the prominent regulator in water and sodium, systemic vasoconstriction, and increased arterial blood pressure. While NPs have been contradicting impact on their functions (counterregulatory) [6].
Myriads of studies suggest that physical training programs have beneficial effects on the integration of cardiovascular functions, but which of plan training are more efficacy and safety is unexplained. Limiting the physiological interpretations of the cardiac responses to RE high-volume in a normal subject, lead to researchers have been accepting current useful influences of resistance training. However, remedial advantages of RE in patients with heart problems probed meticulously in relation to the standardization of exercise programs [7-9], But, in individuals who are healthy this subject is infrequent and widely believed that resistance activities are harmless, while it is not without untold damage to the active individuals. Moreover, different kinds of volumes during RE protocols also can be profited for the assessment of inappropriate or abnormal signs and could give us important insights about prediction the threats [7,9]. Moreover, the consequences of increased muscle mass as a result of RE causes a decrease in high-prevalence disease relevant to obesity and multiple metabolic cardiovascular risk factors [10]. To date, the documents indicate that RE is a major component of an exercise program for the refinement of metabolic derangements and preventing metabolic diseases. This data endorsement by the American Diabetes Association [11], American College of Sports Medicine [12] and American Heart Association [9]. Nevertheless, some studies show that cardiac functions associated with intensive RE be to stand on a continuum between normal and pathophysiological [13,14].
Similarly, other research confirmed unfavourable effects of RE on central arterial compliance [15], blood pressure and cardiac afterload pressure during high-intensity RE protocols [16]. The evidence illustrates that prolonged RE program diminished intrinsic cardiovascular risk factors and promoting cardiac functions are remains ambiguously [17-19] whereas, an explanation has not been considering to depict these contradictions.
The other obvious attraction of study was no investigation that examines the alteration of NPs to RE high-volume. In spite of this, RE is an indispensable part of enhancing musculoskeletal aspects and, it is widespread exert in all sports. Therefore, emphasizing upon the volume of RE is essential because suggestion based on high-intensity or high-volume might be contributing to some of the on-going cardio-myopathy conditions [20,21]. Nevertheless, the purpose of the present study is a closer look at this notion, whether RE with high-volume could lead to adverse cardiac effects through fluctuations in pro-ANP, NT-pro-BNP, ANG-II, NEFA, and Glycerol.
Materials and Methods
Approach to the problem
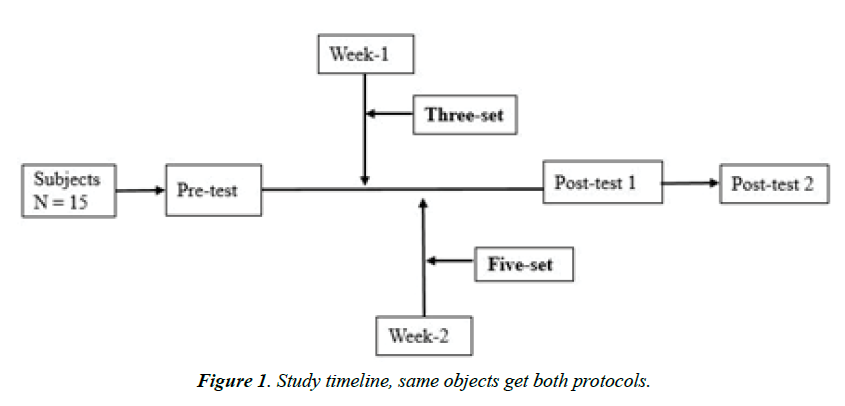
Subjects were allowed to warm-up for 10 minutes with lowintensity treadmill running then performed one repetition maximum (1-RM) for an estimated 10- repetition maximum (10-RM) for eight movements (4 upper and 4 lower body) on the extra session workout. Then, after determining the amount of displaced weight in each item, the subjects performed two different resistance exercise protocols with fluctuation in set frequencies but not exchange in intensity (Table 1). Accordingly, all subjects were performed the 3-set protocol then 5-set protocol by the following the week.
| Movements | Protocol-1 (three-set) | Protocol-2 (five-set) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intensity/ Repetition × Set (10-RM) | Load (kg) | Intensity/Repetition × Set (10-RM) | Load (kg) | |
| Flat bench press | 80/10 × 3 | 45.13 ± 7.9 | 80/10 × 5 | 39.25 ± 2.31 |
| Knee extension | 80/10 × 3 | 29.11 ± 3.0 | 80/10 × 5 | 21.11 ± 1.89 |
| Lat-pull down | 80/10 × 3 | 32.10 ± 0.5 | 80/10 × 5 | 28.67 ± 2.76 |
| Lying hamstrings-curl | 80/10 × 3 | 43.38 ± 4.1 | 80/10 × 5 | 37.83 ± 3.62 |
| Biceps preacher curl | 80/10 × 3 | 34.11 ± 7.9 | 80/10 × 5 | 30.12 ± 2.19 |
| Leg- press | 80/10 × 3 | 134.30 ± 7.3 | 80/10 × 5 | 107.53 ± 8.1 |
| Triceps push-down | 80/10 × 3 | 20.45 ± 3.2 | 80/10 × 5 | 18.29 ± 1.29 |
| Squat | 80/10 × 3 | 65.19 ± 7.0 | 80/10 × 5 | 56.21 ± 4.92 |
Table 1. Resistance exercises.
Note. Inter-set rest (45-sec), and Outer-Set rest (180-sec). The means was reported in each protocol based on the maximum weight that each person only performed in 10-repetition, and for each set (three-set or five-set) average was recorded, eventually total mean calculated from averages.
Subjects
Fifteen active physical education male students (age, 26.1 ± 0.1 yrs. BMI, 22.9 ± 1.09 kg·d-1) after filling out a consent form and confirmed health medication participated in this study each of the subjects were a competitive athlete in various fields of university sports. Also, at the time of the implementation of the research project, none of them were in their own training courses.
Procedures
In both exercise sessions, three blood samples were collected. firstly, prior to the exercise. it has been taken in fasting and after 8 hours of sleep to determine the reference point of the variables. Secondly, 3-minutes after the performance of the resistance exercise because of latency response variables from tissue to the blood. Thirdly and finally, after 30 minutes. In order to follow-up the variables, and probable adjusted responses as a result of their persistence changes or adaptations. Due to the use of statistical cross-design set up, and the pre-test, post-test, and follow-up were run in two separate sessions with a one-week interval accordingly (Figures 1A and 1B).
To measure the amount of cardiac natriuretic peptides and angiotensin-II used Elisa methods, respectively (The pro-ANP plasma levels, ELP kit ANP Pro, Biomedicine, Vienna, Austria. The sensitivity of the method was 0.05 nmol/li-1. The percentage of changes in the test within the test was 4.2%. NT-pro-BNP plasma level, pro-BNP NT-ELITE kit, Biomedicine, Vienna, Austria, the sensitivity of the method used was 3 femto moles per ml, equivalent to 3 picomoles per liter or 3 picomars. The percentage of changes in the test within the test was 3.5%. Ang- II Plasma level, Ang-II Kit, USCN Company, US Department of Commerce. The sensitivity of the method was 3.9 pg/ml. The percentage of changes in the test within the test was 6.7%).
To measure the amount of lipid profile used chemical colorimetric methods respectively (NEFA plasma level, colorimetric kit, AUCO, Germany. The sensitivity of the method was 0.05 mmol/ L. The percentage of changes in the test within the test was 1.7% level of triglyceride, TG, Tricyclic glycerol chromatography kit, Pars Tesh Co., Tehran, Iran. The sensitivity of the procedure was 1 mg / dL. The percentage of changes in the test within the test was 3.2%).
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk test, Twoway Analysis of Variance, and Bonferroni Post-hoc test at a significant level (P ˂0.05) via SPSS software. Before comparing the effects of two resistance protocols, resting data (pre-test each week) tested via depended T-test, regarding the reference point of variables. We only observed the difference in the Ang-II at the baseline; therefore we control the effect of resting levels of this variable through evaluation of Analysis of Co-variation (ANCOVA).
Results
Shapiro-Wilk test indicated that assumption of normality exist in all of plasma data (P> 0.05), also homogeneity of variances was confirmed by the Leven s test. Analyses of variances used to explanation hypothesis of the effects of different volume (threeset × five set) or interaction of resistance exercise significance effects not observed but time effect in each cardiac hormone and lipolysis have demonstrated significant differences (Table 2).
| Variables | Time points | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference point | 3-min after exercise | 30-min after exercise | |||||
| Three-set | Five-set | Three-set | Five-set | Three-set | Five-set | p-value | |
| pro-ANP plasma | 0.75 ± 0.3 | 0.79 ± 0.4 | 1.23 ± 0.7* | 1.29 ± 0.7 | 0.90 ± 0.5 | 1.05±0.50 | 0.294 |
| NT-pro-BNP plasma | 6.98 ± 2.6 | 5.66 ± 2.9 | 7.1± 081 | 6.34±2.4≠ | 7.65 ± 3.6 | 8.47±1.8 | 0.041 |
| Angiotensin-II Plasma | 28.12 ± 25.2¥ | 23.9 ±18.1 | 27.76 ± 17 | 21.17 ±34 | 27.33 ± 20 | 20.93±16 | 943 |
| NEFA plasma | 129.5 ± 30 | 136.73±40 | 123.19 ± 20 | 99.97±2ẟ | 129.86 ± 28.8 | 98.88±26 | 0.157 |
| Triglyceride plasma | 58.19 ± 13 | 56.6 ± 101 | 61.11 ± 3.6 | 62.7±8.1€ | 54.6 ± 7.3 | 52.9±7.2 | 0.604 |
Table 2. Plasma variables measured.
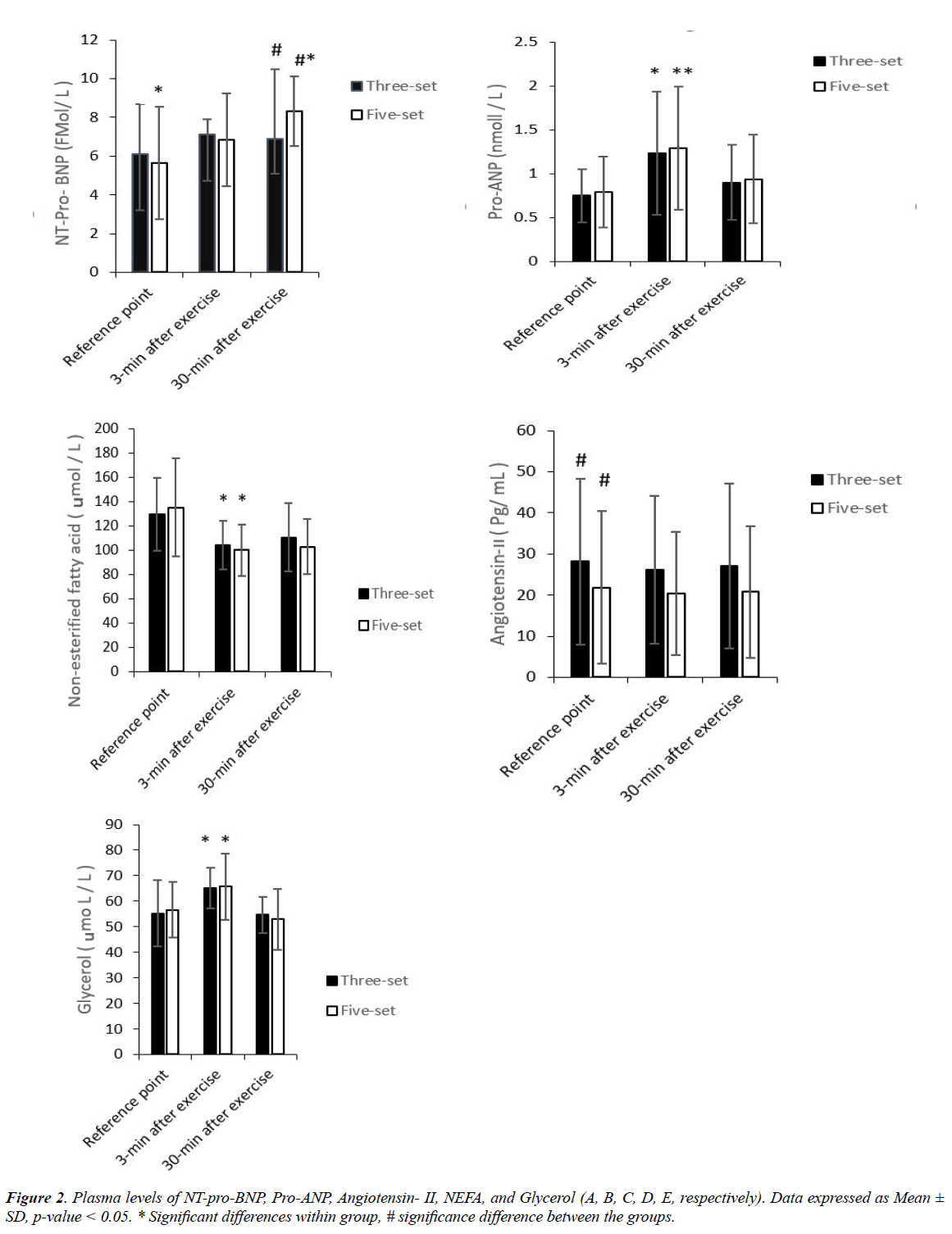
Increase natriuretic peptides concentration during both protocols (Figures 2A and 2B) indicate that cardiac more sensitive to RE. Data analyze of ANP confirmed that volume of RE has not meaningful effects (interaction, p=0.294, F28,2=1.198) but in consideration of time effects (Time, p=0.001, F28,2=20.128) significant value observed. NT-pro-BNP concentration in fiveset has a significant increase compare to three- set (interaction, p=0.041, F28, 2=8.103). Also in consideration of within group just five- set has meaningful increased (Time, F14, 1=5.731, p=0.044).
To examine angiotensin data (Figure 1C) t- test analyze indicate that resting level has significant different (reference points, T28=2.413, p=0.003). Therefore, co-variate analyzed usage to determine real differences impacts of protocols. Then due to elimination effects of resting concentration of angiotensin, data has no meaningful changes due to RE volumes (F23, 1=0.005 p=0.943) also in consideration of each time points in both protocols, decreases in angiotensin not reach to significance (within group, F20, 2=0.205 P=0.817).
None-esterified fatty acid and glycerol (lipolysis markers, Figure 1C, 1D, 1E) in response to RE volumes have a revers fluctuation. NEFA data due to five set protocols has not a meaningful decrease compare to three- set (interaction, F20, 2=4.3, p=0.157) subsequently time effects (F20, 2=6.77, p=0.006) was significant (within time point). Glycerol data analyze indicate that volumes of RE has no significant effects (between group, F13, 1=0.146, p=0.604) but time effects increase in glycerol was meaningful (within group, F26, 2=13.976, p=0.001).
Discussion
In 2019, interest in resistance exercise (RE) plan work outboth the recreational and professional varieties- has grown dramatically. In particular, intensive RE programs have been performed widespread among adolescent [22]. The present study demonstrates that RE high-volume associated with significantly increased in the concentration of the N-terminal fragment of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP). Bulk of studies demonstrates that increased in NT-pro-BNP identified as a hallmark for heart attack [23-25] (deeply discussed below). On the other hand, high-volume RE has no significant effect on the increased plasma levels of ANP and decrease angiotensin- II at each time point. Further, lipolysis concentrations (NEFA and Glycerol) in response to both protocols (high-volume, low-volume) altered significantly without differences between protocols.
Most relevance mechanism about increment in plasma ANP due to exercises is increased in the myocardial stretch as a result of raised in blood venue return [26,27]. Albeit, the resistance exercise cause elevated in intrathoracic pressure leading to decrease venous return and cardiac output [28]. The logical explanation for an increase in ANP can be drastically blood venous return during rest periods (reperfusion). recent studies also verified increase release of ANP in response to one session RE in variety populations (healthy, athlete, patient, and elder) [29,30].
Although research on BNP has been considered in pathophysiological conditions extensively than the physiological. Apparently, increases in BNP have determined to compensatory responses to defeat pathophysiological induces [31]. But results in healthy and patient subjects could have been differing meaning. It was providing that risen plasma levels of NT-pro-BNP at the pathophysiological conditions stimulated from intrinsic cardiac risk factors such as to impair excitationcontraction coupling [24,31]. While in physiological conditions increase in BNP occurred through extrinsic factors such as increased End-diastolic volume during exercises and usually not related to maladaptive processes [32]. But cardiovascular exogenous factors can also disrupt physiological conditions at certain times. When the magnitude of volume load on the cardiovascular system will be vigorously. For example, set frequencies and subsequently repetitions are dramatically [33]. Related evidence has focused on whether exhausted protocols which associated with substantially increases in NPs could a reflector of myocardial damage in athletes [25]. Because, evidence revealed that several cases of sudden cardiac death due to cardiovascular problems have been reported in athletes [34] To the document of exercise-induced myocardial damage, referred to Scharhag et al. [35] work in healthy athletes, twenty young male athletes performed exhausted protocols. Myocardial damage was evaluated by echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging, in addition, the level of cardiac troponin-I and NT-pro-BNP significantly increased [35]. Moreover, circulating levels of the (NT-pro-BNP) reflect left ventricle diastolic wall stress and are strong predictor of sudden death and mortality in chronic heart failure [24]. Hence, we remained that one session RE high-volume must be taken into consideration for prevention immediate hazardous cardiac events, resulted in suddenly raised in NT-pro-BNP [36].
Again, evidence have shown that greater amount of NT-pro- BNP > 400 Pg/mL associated with symptoms of heart failure [37] which pretend in both parametrical measurements such as drop proportion E/A (peak velocity blood flow from gravity in early diastole to peak velocity blood flow in late diastole caused by atrial contraction, also decrease E/A ratio accompanied by diminished lusitropic and left ventricle function) and structural cardiac remodeling. Results in abnormal diastolic distensibility the optimal exercise programs to prevent these disorders in healthy individual necessary to be excluded. Thus, we illustrated that cardiovascular implications might have been occurring in normal humans, when we ignored the volume of RE. More speculate, routine and persistently training programs in athletes caused overtraining. These effects particularly occurred in the heart parameters such as increase resting heart rate, catecholamine oversecretion and decrease stroke volume and parasympathetic releasing. Finding present study suggest that an extraordinary elevation in NPs during high-volume RE might be trigger of overtraining which is one of the markers that correlated to over-training in athletes. Because, experimental studies proven that an increased in the NT-pro-BNP at least one week requires to return to their reference point. Besides, longer half-life of plasma NT-pro-BNP rather than the ANP, (⁓ sevenfold) [38] is another reason for controversial disagreement in the present study. Among the overwhelming research of resistance training in healthy subjects, there have been no reported cardiovascular implications. In that case, the effects of exercise on NPs and the underlying mechanism of exerciseinduced NPs secretion in athletes, young and healthy subjects remain unknown. It would be originated from the identical and standard resistance protocols.
The renin angiotensin system interacts conversely with circulating levels of cardiac peptides. The importance of Ang is attribute to dwindle in the renal blood flow (RBF) [6] thus, slightly decreases during exercise causes enhancement in vasodilation and natriuresis. Truly, we have pointed out intervening of difference volume of RE lead to similar decrease in angiotensin- II.
Data regarding to the effects of RE and increases muscle mass on lipid metabolism are more pronounced. Recently, investigation declared the improvement of lipid mobilization by mediating of NPs in humans’ fat cells [39]. studies illustrate that they are major regulator of lipolysis during prolonged exercises [5]. Although, free fatty acid the main substrate for cardiac metabolism. The uninterruptedly increased of FFA from adipose tissue might have caused myocardial lipotoxicity, which can contribute to decline in cardiac effectiveness [40]. At the present work, indicated that lipolysis significantly increased immediately after both protocols. However, non-esterified fatty acid diminishing meaningfully. That shown higher demanding of active tissues especially cardiac and skeletal muscle to energy productivity.
Practical Applications
NPs are most validity biomarkers among all hemodynamic and intrinsic cardiac factors. Thus, during exercises they are wellstablished for influencing filling pressure and cardiac capability [23] in responses to stimuli such as augmented cardiac pressure, volume overload and wall tension [41].
Conclusion
In conclusion, high-volume of resistance exercise may contribute to opposite effects on cardiac via elevated blood pressure and increase myocardial works, which it is leading to over secretion of NT-pro-BNP.
References
- Levin ER, Gardner DG, Samson WK. Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339(5):321-328.
- Goetze JP, Christoffersen C, Perko M, et al. Increased cardiac BNP expression associated with myocardial ischemia. FASEB J. 2003;17(9):1105-1107.
- Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, et al. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(3):161-167.
- Alehagen U, Lindstedt G, Levin LÅ, et al. Risk of cardiovascular death in elderly patients with possible heart failure: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and the amino-terminal fragment of ProBNP (N-terminal proBNP) as prognostic indicators in a 6-year follow-up of a primary care population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005;100(1):125-133.
- Bartels ED, Guo S, Kousholt BS, et al. High doses of ANP and BNP exacerbate lipolysis in humans and the lipolytic effect of BNP is associated with cardiac triglyceride content in pigs. Peptides. 2019;112: 43-47.
- Sarzani R, Salvi F, Dessì-Fulgheri P, et al. Renin–angiotensin system, natriuretic peptides, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and hypertension: an integrated view in humans. J Hypertens. 2008;26(5):831-843.
- Fletcher GF, Ades PA, Kligfield P, et al. Exercise standards for testing and training: J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;128(8): 873-934.
- Thompson PD. Exercise prescription and proscription for patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2005;112(15): 2354-2363.
- Pollock ML, Franklin BA, Balady GJ, et al. Resistance exercise in individuals with and without cardiovascular disease: benefits, rationale, safety, and prescription an advisory from the committee on exercise, rehabilitation, and prevention, council on clinical cardiology. J Am Heart Assoc. 2000;101(7): 828-833.
- Poehlman ET, Dvorak RV, De-Nino WF, et al. Effects of resistance training and endurance training on insulin sensitivity in nonobese, young women: A controlled randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(7):2463-2468.
- Sigal RJ, Kenny GP, Wasserman DH, et al. Physical activity/exercise and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes care. 2004;27(10): 2518-2539.
- Pescatello LS, Franklin BA, Fagard R, et al. Exercise and hypertension. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(3): 533-553.
- Pluim BM, Zwinderman AH, van der Laarse A, et al. The athlete’s heart: a meta-analysis of cardiac structure and function. Circulation. 2000;101(3):336-344.
- Maron BJ. The Athlete's Heart and Cardiovascular Disease. WB Saunders; 1997.
- Miyachi M, Kawano H, Sugawara J, et al. Unfavorable effects of resistance training on central arterial compliance: a randomized intervention study. Circulation. 2004;110(18):.2858-2863.
- Jürgenson J, Serg M, Kampus P, et al. The effect of pre-seasonal strength training on central hemodynamics and cardiac function in elite powerlifting athletes. Clin Res Cardiol. 2019; 10:33-41.
- Braith RW, Stewart KJ. Resistance exercise training: its role in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2006;113(22):2642-2650.
- Figueroa A, Okamoto T, Jaime SJ, et al. Impact of high-and low-intensity resistance training on arterial stiffness and blood pressure in adults across the lifespan: A review. Pflügers Archiv- Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019;471(3): 467-478.
- Stöhr EJ, Stembridge M, Esformes JI. In vivo human cardiac shortening and lengthening velocity is region dependent and not coupled with heart rate: ‘longitudinal ‘strain rate markedly underestimates apical contribution. Exp Physiol. 2015;100(5):507-518.
- Fagard R. Athlete’s heart. Heart. 2003;89(12):1455-1461.
- Boraita A, Sánchez-Testal MV, Diaz-Gonzalez L, et al. Apparent ventricular dysfunction in elite young athletes: another form of cardiac adaptation of the athlete's heart. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019;32(8):987-996.
- Faigenbaum AD, French DN, Lloyd RS, et al. Strength and power training for young athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2019:131-154.
- Palazzuoli A, Beltrami M, Ruocco G, et al. The role of natriuretic peptides for the diagnosis of left ventricular dysfunction. Sci World J. 2013;2013.
- Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, et al. Plasma natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med 2004;350(7):655-663.
- Faviou E, Zachari A, Nounopoulos C, et al. Elevation of serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide after exercise is an index of myocardial damage or a cytoprotective reflection? J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2008;48(1):90.
- Huang WS, Lee MS, Perng HW, et al. Circulating brain natriuretic peptide values in healthy men before and after exercise. Metabolism-Clinical and Experimental. 2002;51(11): 1423-1426.
- Whyte JJ, Harold Laughlin M. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on the vasculature. Acta Physiol Scand. 2010;199(4): 441-450.
- Harman EA, Frykman PN, Clagett ER, et al. Intra-abdominal and intra-thoracic pressures during lifting and jumping. Army Research Inst of Environmental Medicine Natick MA; 1987.
- Siegel AJ, Lewandrowski EL, Chun KY, et al. Changes in cardiac markers including B-natriuretic peptide in runners after the Boston marathon. Am J Cardiol. 2001;88(8):920-923.
- Ohba H, Takada H, Musha H, et al. Effects of prolonged strenuous exercise on plasma levels of atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide in healthy men. Am. Heart J. 2001;141(5): 751-758.
- Thireau J, Karam S, Roberge S, et al. β-Adrenergic blockade combined with subcutaneous B-type natriuretic peptide: A promising approach to reduce ventricular arrhythmia in heart failure? Heart. 2014;100(11):833-41.
- Pathak V, Aris R, Jensen BC, et al. Effect of 6-min walk test on pro-BNP levels in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Lung. 2018;196(3): 315-319.
- Kingsley JD, Figueroa A. Acute and training effects of resistance exercise on heart rate variability. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2016;36(3): 179-187.
- Semsarian C, Sweeting J, Ackerman MJ. Sudden cardiac death in athletes. Bmj. 2015;18:350.
- Scharhag J, Urhausen A, Schneider G, et al. Reproducibility and clinical significance of exercise-induced increases in cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide in endurance athletes. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2006;13(3): 388-397.
- Calzetta L, Orlandi A, Page C, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide: much more than a biomarker. Int J Cardiol. 2016;221: 1031-1038.
- Conraads VM, Beckers P, Vaes J, et al. Combined endurance/resistance training reduces NT-proBNP levels in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2004;25(20):1797-1805.
- Schlueter N, de Sterke A, Willmes DM, et al. Metabolic actions of natriuretic peptides and therapeutic potential in the metabolic syndrome. Pharmacol Ther.2014;144(1):12-27.
- Moro C, Polak J, Hejnova J, et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide stimulates lipid mobilization during repeated bouts of endurance exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;290(5):864-869.
- Von Haehling S, Lainscak M, Springer J, et al. Cardiac cachexia: a systematic overview. Pharmacol Ther 2009;121(3):227-252.
- Metra M, Dei Cas L, Bristow MR. The pathophysiology of acute heart failure--it is a lot about fluid accumulation. Am Heart J. 2007;155(1):1-5.