Page 18
allied
academies
Journal of Materials Science and Nanotechnology | Volume: 3
March 20-21, 2019 | London, UK
Materials Science and Materials Chemistry
2
nd
International Conference on
E
stablishment of an efficient method for distribution of
electric power is a key to realize a sustainable society
which is driven with renewable-energy-based electricity. We
demonstrate highly efficient power storage using an alcohol/
carboxylic acid redox couple. Glycolic acid (GC), a monovalent
alcoholic compound and oxalic acid (OX), a divalent carboxylic
acid, are focused as a redox couple due to their stability
and transportability as energy-storage media. We achieved
high Faradaic efficiencies for the production of GC from
OX on ubiquitous TiO
2
catalysts under mild conditions. The
most desirable characteristic of this electro-reduction is the
suppression of hydrogen evolution even in acidic aqueous
media. TEM-EELsmapping for TiO
2
catalysts revealed thatwhole
grain of an active catalyst is composed only of an anatase phase
whereas a rutile phase forms on the surface of an inactive one,
which suggests that detailed structural control is significantly
predominant in this process. Recently, we succeeded in the
production of GC via the electrochemical reduction of OX
with the help of renewable light energy and continuous GC
production using a polymer electrolyte alcohol electrosynthesis
cell (PEAEC) for the first time.
Speaker Biography
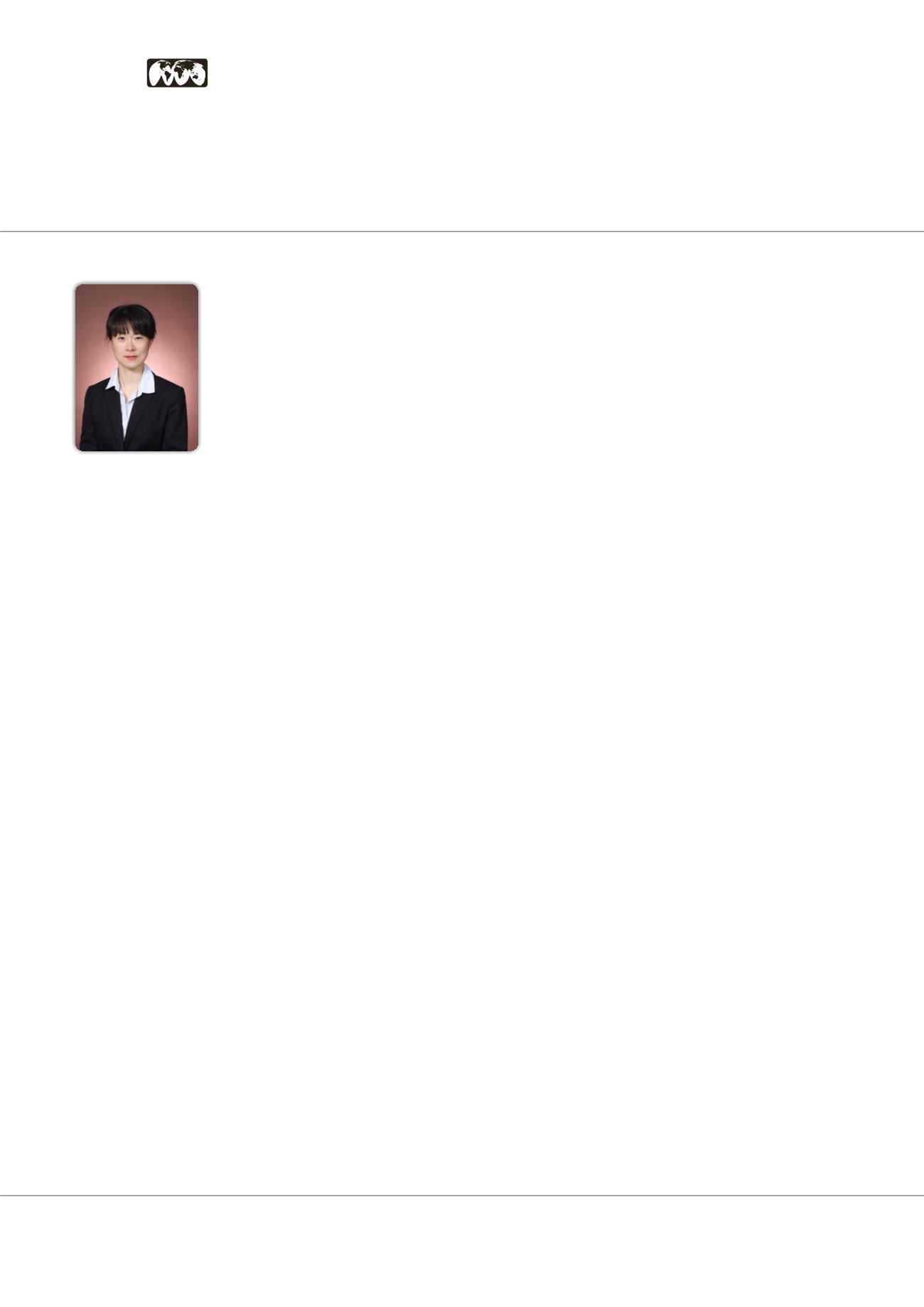
Miho Yamauchi received her PhD in 2001 from Tsukuba University, Japan. She is currently
a professor and principal investigator of catalytic materials transformation division in
WPI International Institute for Carbon-Neutral Energy Research (WPI-I2CNER), Kyushu
University, Japan.
e:
yamauchi@i2cner.kyushu-u.ac.jpMiho Yamauchi
Kyushu University, Japan
Inorganic nanocatalysts for efficient power storage into liquid