allied
academies
OBESITY AND WEIGHT MANAGEMENT
VACCINES AND IMMUNOLOGY
&
International Conference on
International Conference on
J u n e 2 8 - 2 9 , 2 0 1 8 | A m s t e r d a m , N e t h e r l a n d s
Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences
|
Volume 8
ISSN:
2249-622X
Page 14
Joint Event on
Statement of the Problem:
The World Health Organization (2017) has recently
reported that worldwide, at least 2.8 million people die each year because of
being overweight or obese, and an estimated 35.8 million (2.3%) of global
disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) are caused by overweight or obesity.
The purpose of this study was to examine identifiable risk factors and disease
outcomes which may be associated with obesity prevalence rates in children
and adult populations.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation:
This study examined inpatient
pediatric patients using the kids´ inpatient database (KID), healthcare cost and
utilization project (HCUP), and the agency for healthcare research and quality.
A large randomly drawn sample (N=524,581) of boys (N=244,553) and girls
(N=280,028) ages five to 12, was examined in this research study to test for
the association between obesity prevalence and disease related outcomes.
Additionally, a small adult sample of adults ages 19 to 55 (N=143), enrolled
in an undergraduate level city college program, were assessed to determine
if there was a relationship between obesity prevalence and the outcomes
of heart disease risk and type 2 diabetes risk. The Pearson Chi Square test
was applied to measure for significant variable associations in this research
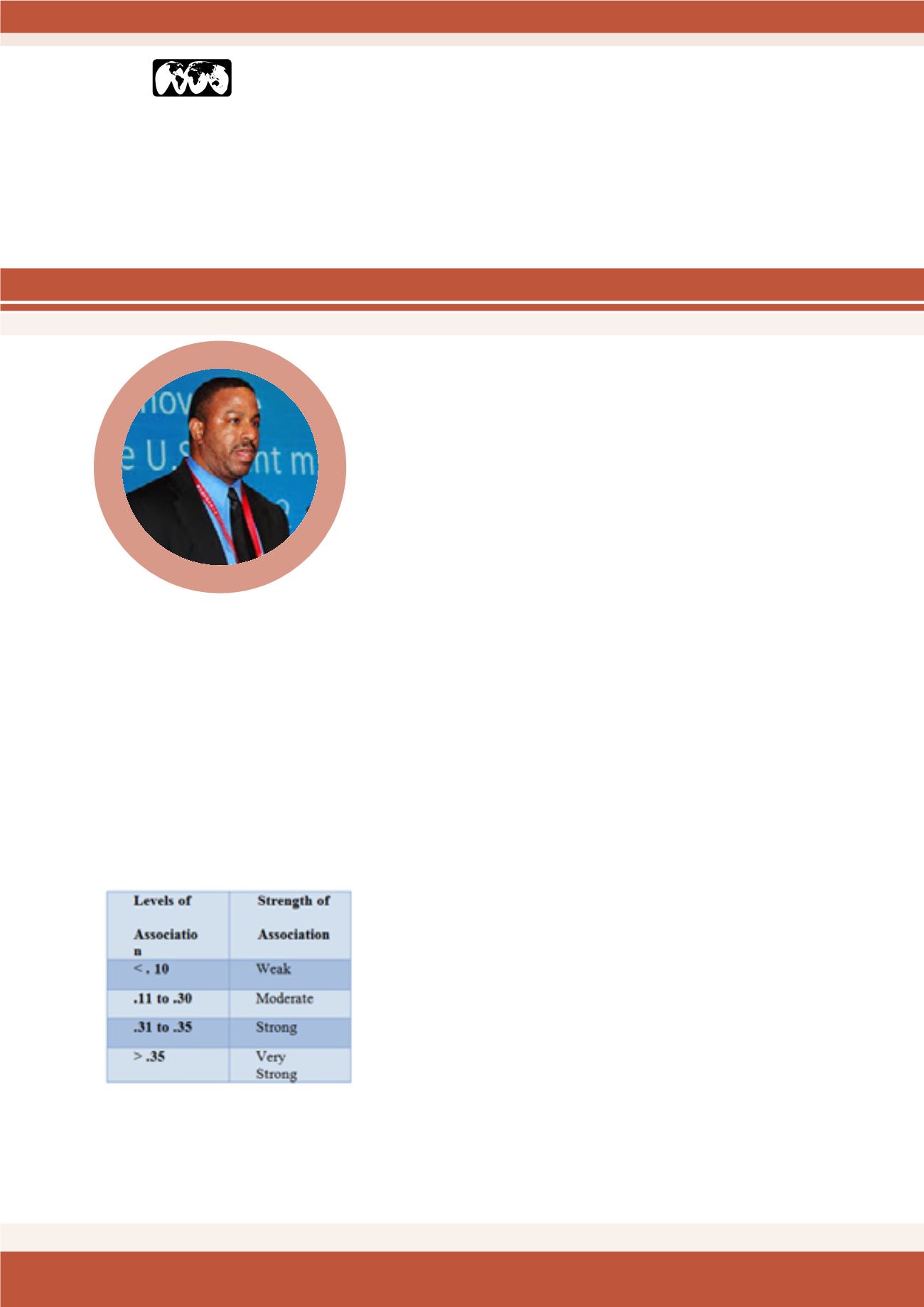
study in addition to the application of the Cramer’s V analysis to examine for
strength of variable associations. A multiple regression analysis was applied
to determine if heart disease risk and type 2 diabetes risk were significant
predictors of obesity prevalence in adult groups.
Findings:
The research found that there were significant associations between
obesity and health outcomes in children (p<0.001) and that the factors of heart
disease risk and type 2. Diabetes risk were significant predictors for obesity
prevalence in adults (p<0.05).
Conclusion & Significance:
The outcome of this research study provides
support for improved efforts to develop more effective strategies to promote
positive healthy lifestyles in adults and children’s populations.
Biography
Damien Byas is a PhD holder and an Epidemiolo-
gist and Professor of Public Health at American
Public Health Association. He is an International
Public Health Delegate and President of North
American Scientific Committee on cardiovascu-
lar health.
Dbyas@arizona.usa.comINVESTIGATING HEALTH OUTCOMES
ASSOCIATED WITH OBESITY RATES
IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS
Damien Byas
Center for Healthcare and Organizational
Research, USA
Damien Byas, Asian J Biomed Pharmaceut Sci 2018, Volume 8 | DOI: 10.4066/2249-622X-C1-001
figure.1: Standard for Cramer’s V and
phi coefficients.